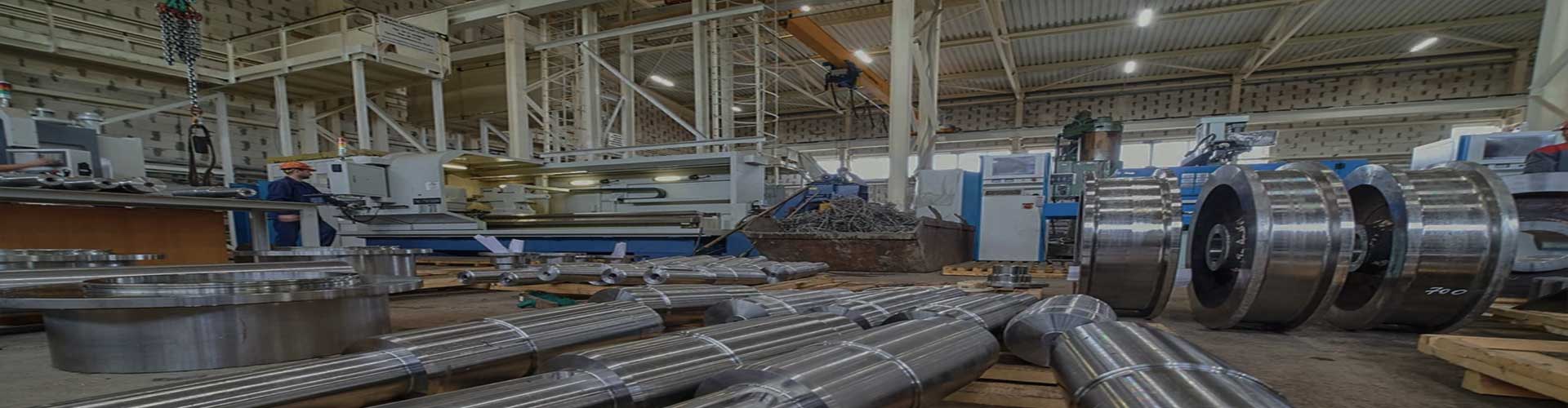
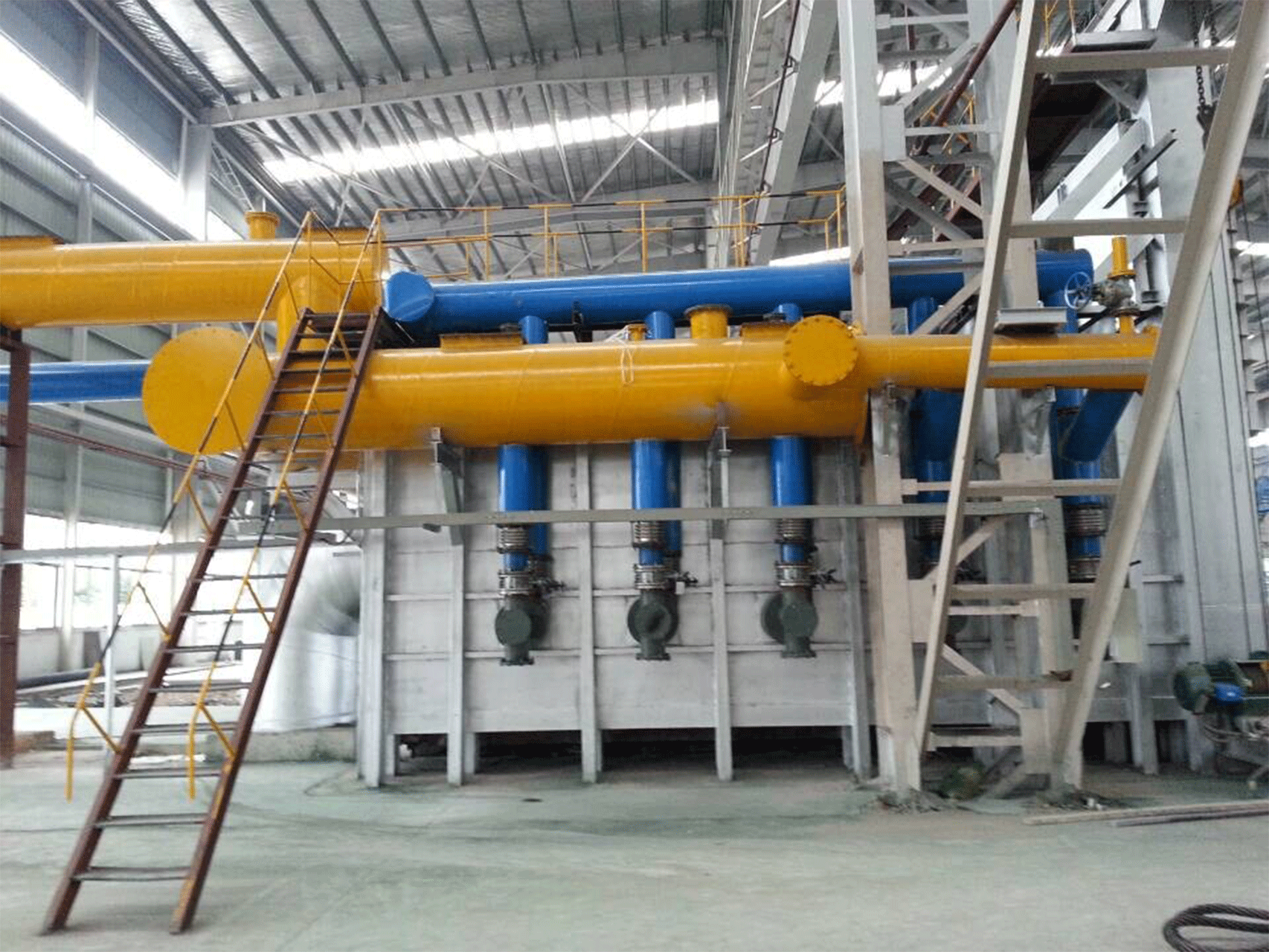
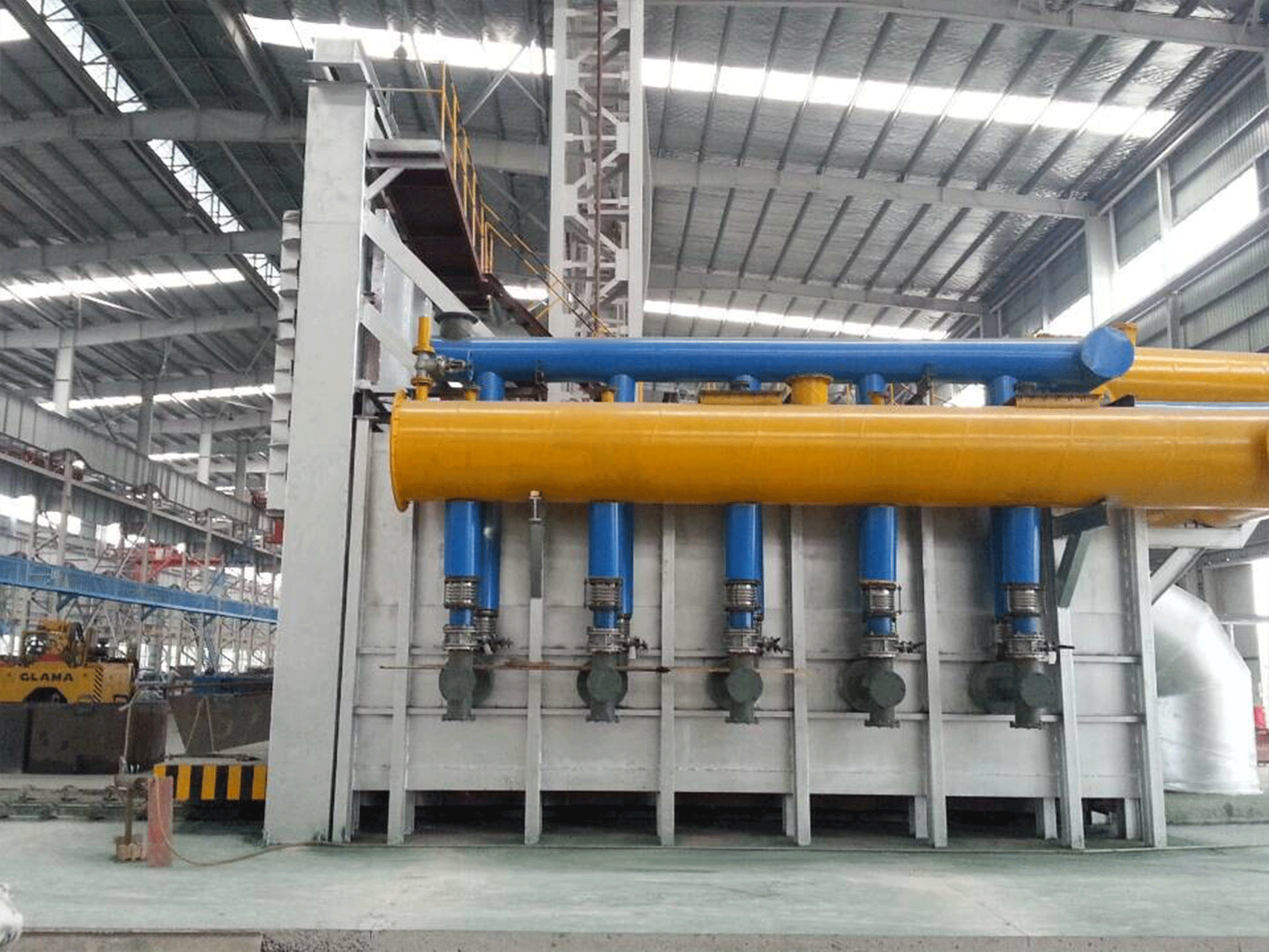
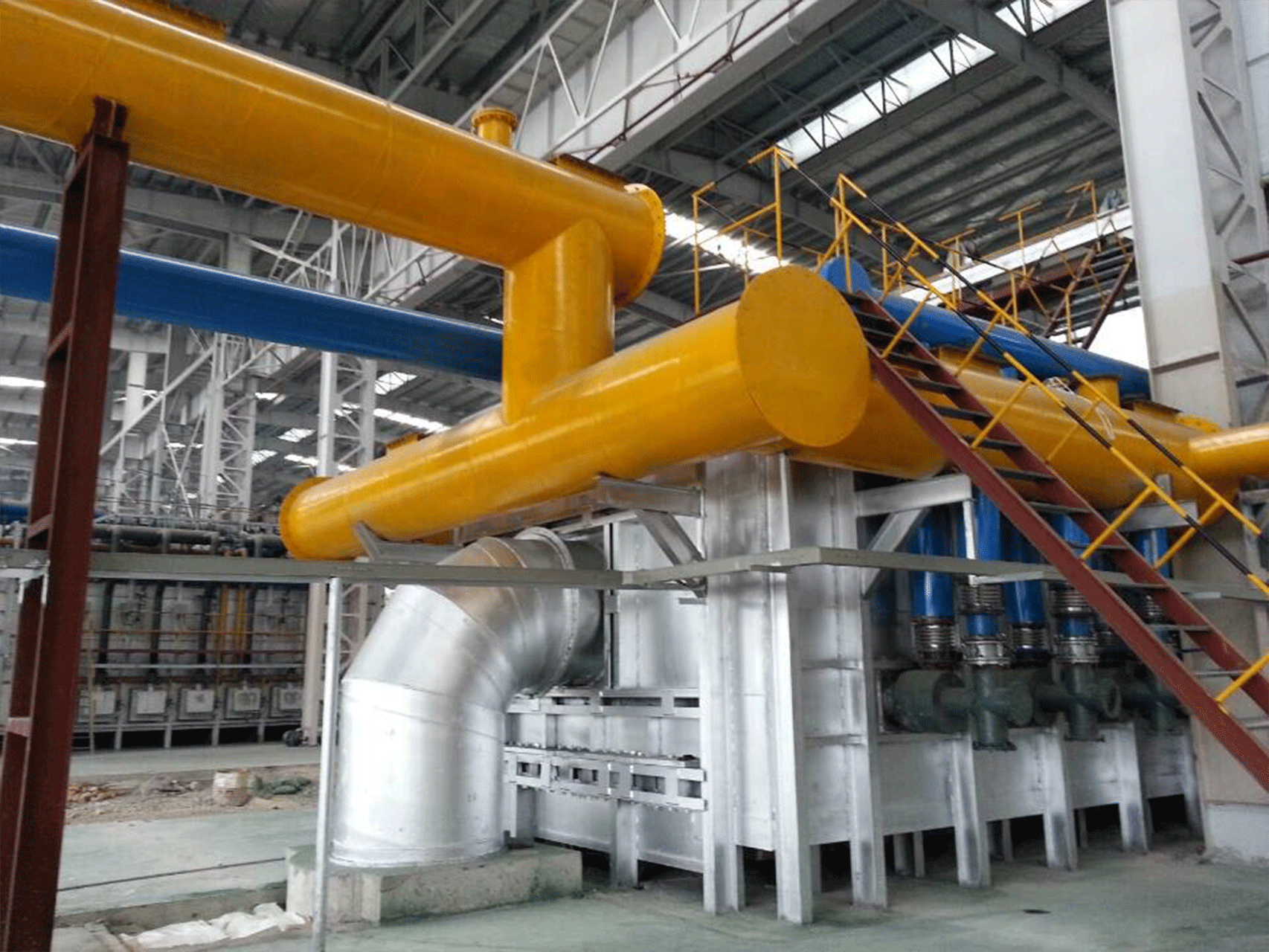
Steel rolling furnace plays a pivotal role in the production of steel sheets and other steel products. These furnaces transform ingots into flat sheets of steel through a complex and precise process. Quality control is of utmost importance in steel rolling furnace operations, as the final product’s quality and performance depend on it.
Understanding the Different Types of Steel Rolling Furnace
Steel rolling furnaces come in various types, each designed for specific applications. JiangSu YiNuo Thermal Energy Technology Co., Ltd., a reputable steel rolling furnace manufacturer, offers several types of furnaces to meet the diverse needs of the industry.
1. Reheating Furnaces:
Reheating furnaces are used to raise the temperature of steel ingots or billets before they enter the rolling process. This pre-heating step is crucial to make the steel more malleable and easier to shape during the rolling operation. Reheating furnaces are available in different designs, such as walking beam and pusher types, each offering unique advantages in terms of energy efficiency and throughput.
2. Rolling Mill Furnaces:
Rolling mill furnaces are specifically designed for the rolling process, where steel is shaped into various forms like bars, sheets, or profiles. These furnaces provide the controlled temperature and environment required for the successful rolling of steel products. They are equipped with advanced automation systems for precise temperature control and rolling speed adjustments.
Understanding the Steel Rolling Furnace Process
Before delving into quality control strategies, it’s essential to understand the steel rolling furnace process. This process involves several stages, including heating, rolling, and cooling, all of which require precision to ensure high-quality steel sheets.
1. Heating: The ingots are first heated in the furnace to a specific temperature. This temperature is crucial for proper rolling, as it affects the steel’s malleability.
2. Rolling: The heated steel is then passed through a series of rolling mills to reduce its thickness and shape it into flat sheets. This stage requires precise control over the rolling speed and pressure.
3. Cooling: After rolling, the steel sheets are cooled to room temperature to stabilize their properties and prevent warping.
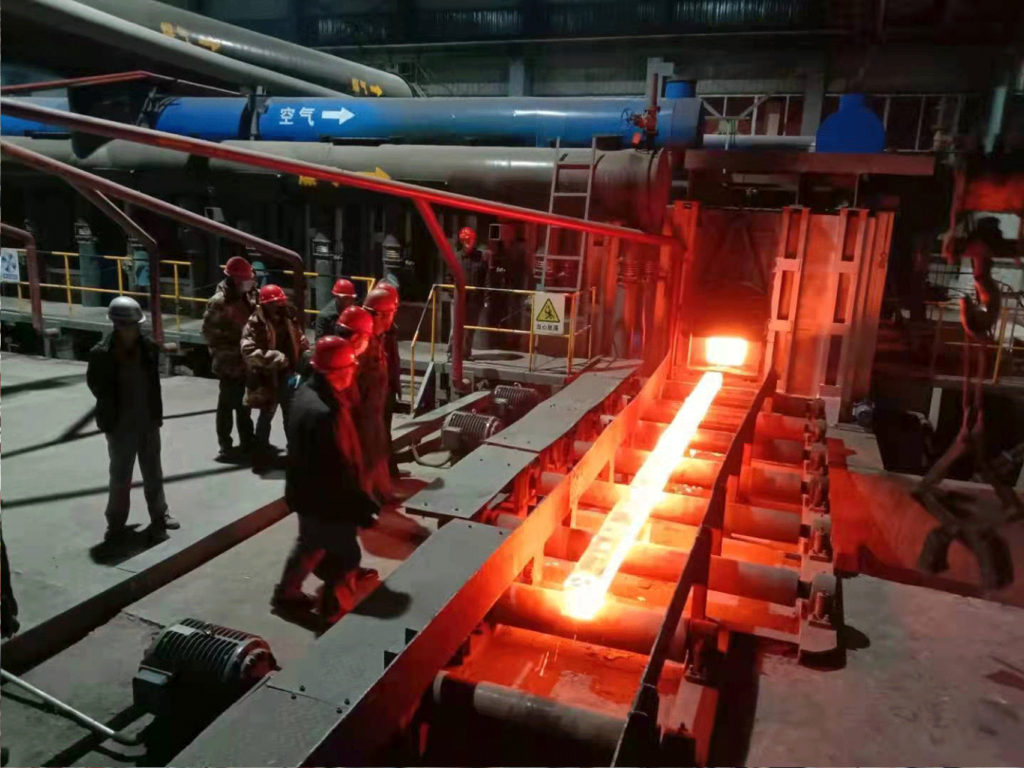

Efficiency Matters: Tips for Optimizing Steel Rolling Furnace Operations
Efficiency is a critical aspect of steel rolling furnace operations. To ensure quality control, manufacturers must optimize their processes. Here are some tips for achieving efficient operations:
1. Temperature Control: Maintaining the right heating temperature in the furnace is essential for a successful rolling process. Advanced temperature control systems, such as those offered by JiangSu YiNuo Thermal Energy Technology Co., Ltd., help regulate the furnace temperature with high precision, minimizing temperature variations and ensuring uniform heating.
2. Rolling Speed and Pressure: The rolling process’s speed and pressure are critical factors affecting the steel’s thickness and surface finish. Modern rolling mills are equipped with automated systems that allow precise control over these parameters. Real-time monitoring and adjustments can help maintain product quality.
3. Cooling Systems: Effective cooling is vital for preventing warping and ensuring the steel’s structural integrity. Quality rolling steel furnace comes with efficient cooling systems that ensure a uniform cooling rate, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
Quality Control Strategies in Steel Rolling Furnace Operations
Achieving consistent quality in steel rolling furnace operations is of utmost importance to steel manufacturers. To ensure this, various strategies and tools are employed:
1. Temperature Control: Steel Rolling Furnace
Maintaining the right temperature is crucial for the rolling process. Inconsistent temperatures can lead to defects in the final product. Advanced temperature control systems, including thermocouples and infrared sensors, are used to monitor and regulate the furnace’s temperature throughout the rolling operation.
2. Material Inspection: Steel Rolling Furnace
Quality control starts with the raw material. Manufacturers must ensure the quality of the steel ingots or billets before they enter the rolling furnace. Advanced testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection, are employed to detect any flaws or impurities in the material, which can affect the final product’s quality.
3. Automation and Process Monitoring: Steel Rolling Furnace
Automation plays a significant role in quality control. Modern steel rolling furnaces are equipped with advanced automation and monitoring systems. These systems can precisely control various parameters, such as furnace temperature, rolling speed, and pressure. Real-time data analysis allows operators to make immediate adjustments when needed.
4. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Steel Rolling Furnace
Non-destructive testing techniques, such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and radiographic testing, are used to check for defects in the steel products after the rolling process. These methods can detect internal flaws, cracks, and surface defects without damaging the finished product.
5. Quality Assurance Programs: Steel Rolling Furnace
Implementing robust quality assurance programs is vital to ensuring consistent quality. Manufacturers often follow international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, and have dedicated quality control teams that monitor and improve processes continuously.
Tools for Quality Control in Steel Rolling Furnace Operations
To facilitate quality control in steel rolling furnace operations, a range of tools and equipment are used. These tools help operators maintain precise control over the process and detect defects in real time.
1. Infrared Temperature Sensors: Steel Rolling Furnace
Infrared sensors provide non-contact temperature measurement, allowing for accurate monitoring of steel’s temperature in the furnace. These sensors can help prevent overheating or underheating, ensuring consistent quality.
2. Remote Monitoring Systems: Steel Rolling Furnace
Remote monitoring systems enable operators to keep a close eye on the furnace’s performance from a control room. They provide real-time data, alarms, and trends, allowing for quick response to any deviations from the desired process parameters.
3. Quality Control Software: Steel Rolling Furnace
Specialized software is used for data analysis and process control. This software can predict potential defects based on historical data and optimize the rolling process to prevent them.
4. Metallographic Analysis: Steel Rolling Furnace
Metallographic analysis involves examining microstructures and grain sizes in steel samples. This can help identify issues like improper cooling rates or material composition deviations, contributing to improved product quality.
5. Continuous Improvement Tools: Steel Rolling Furnace
Quality control is an ongoing process. Continuous improvement tools like Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) help identify and eliminate process inefficiencies and variations, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of the steel products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quality control in steel rolling furnace operations is a multifaceted process that relies on a combination of technology, skilled operators, and meticulous attention to detail. Manufacturers, such as JiangSu YiNuo Thermal Energy Technology Co., Ltd., provide advanced equipment and tools that enable precise control and monitoring of the rolling process, ensuring the production of high-quality steel sheets. By implementing efficient and effective quality control strategies, manufacturers can meet the demands of various industries that rely on steel products while maintaining their reputation for excellence in steel rolling furnace operations.