Inquiry
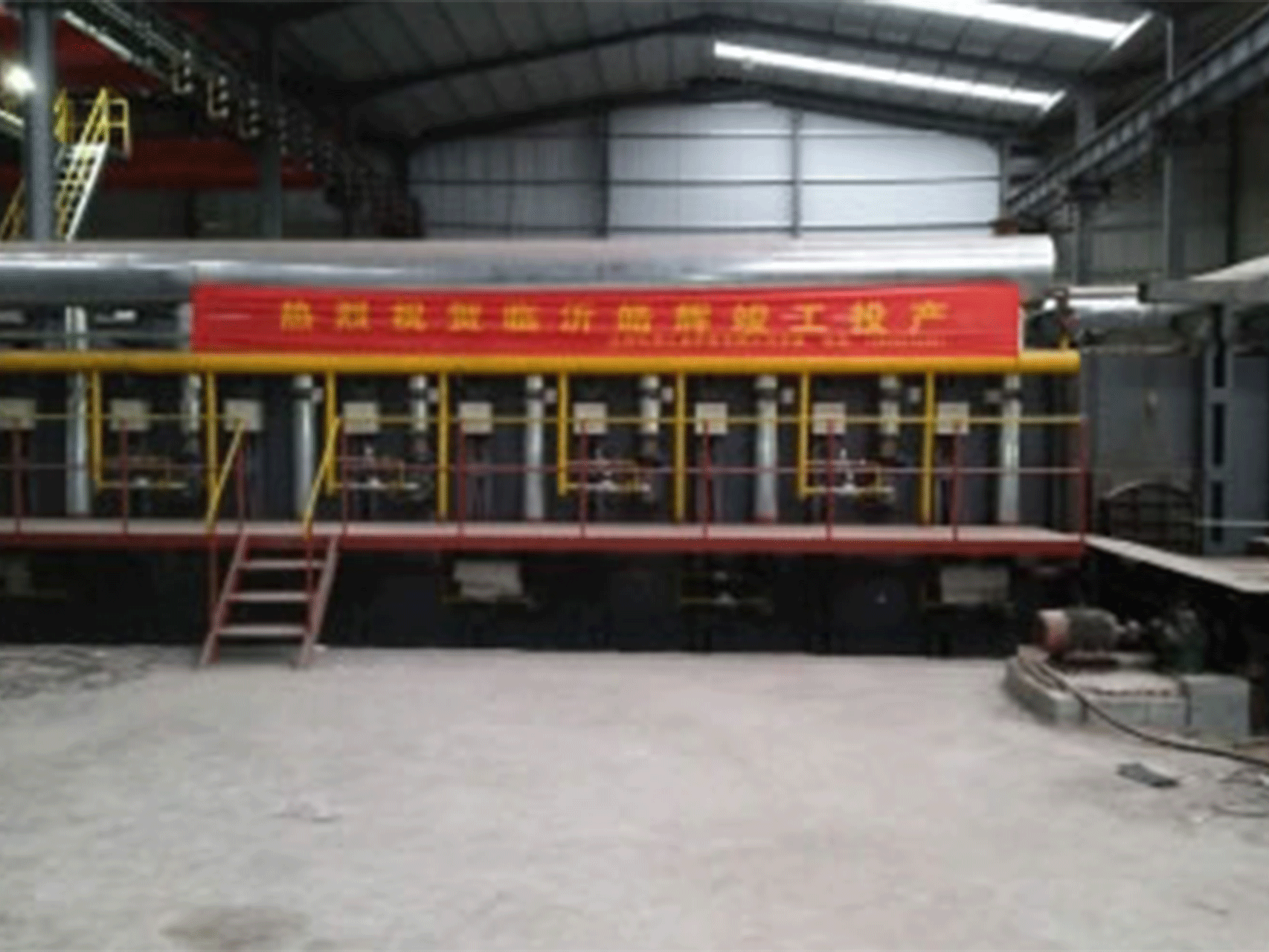
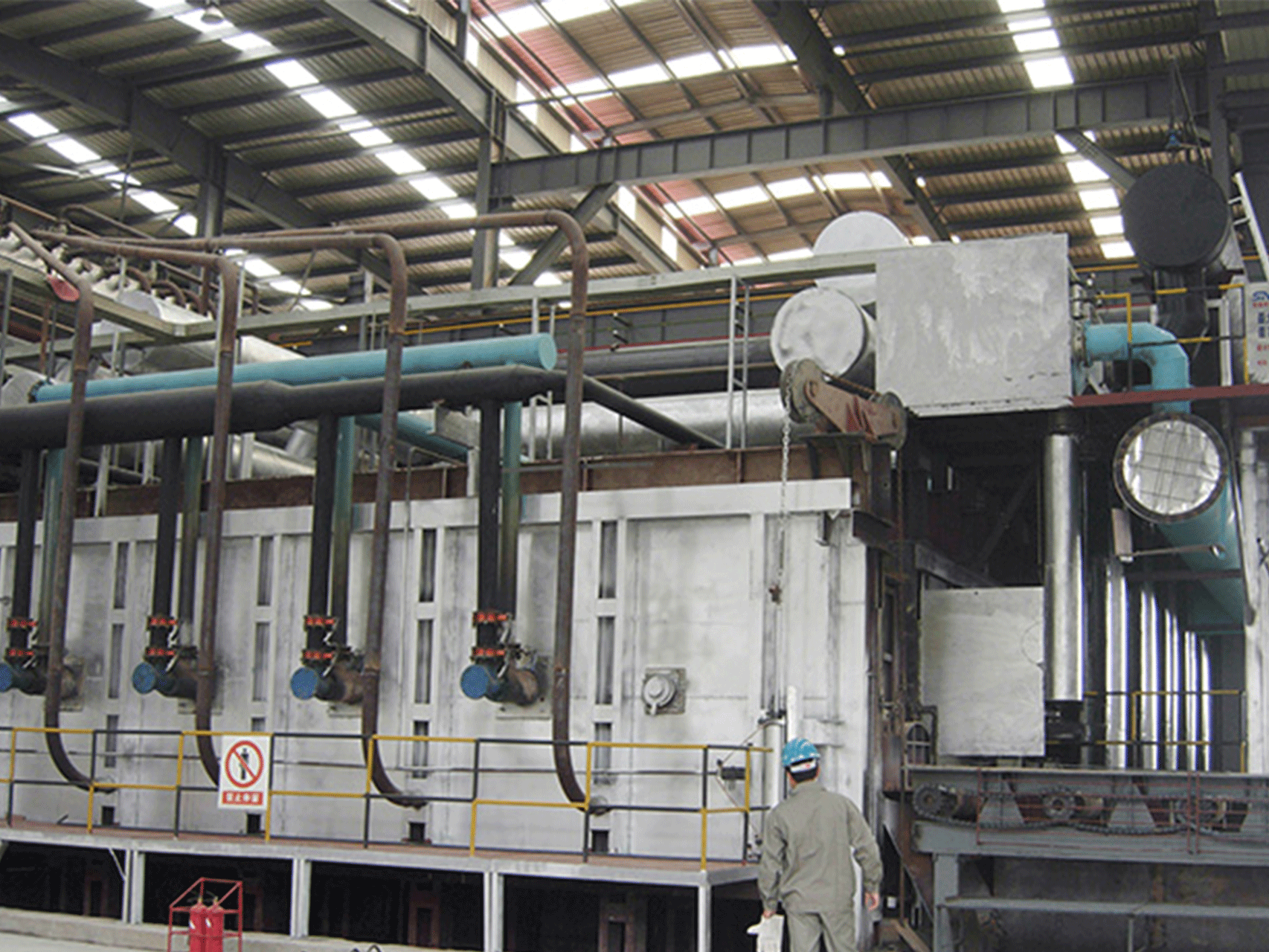
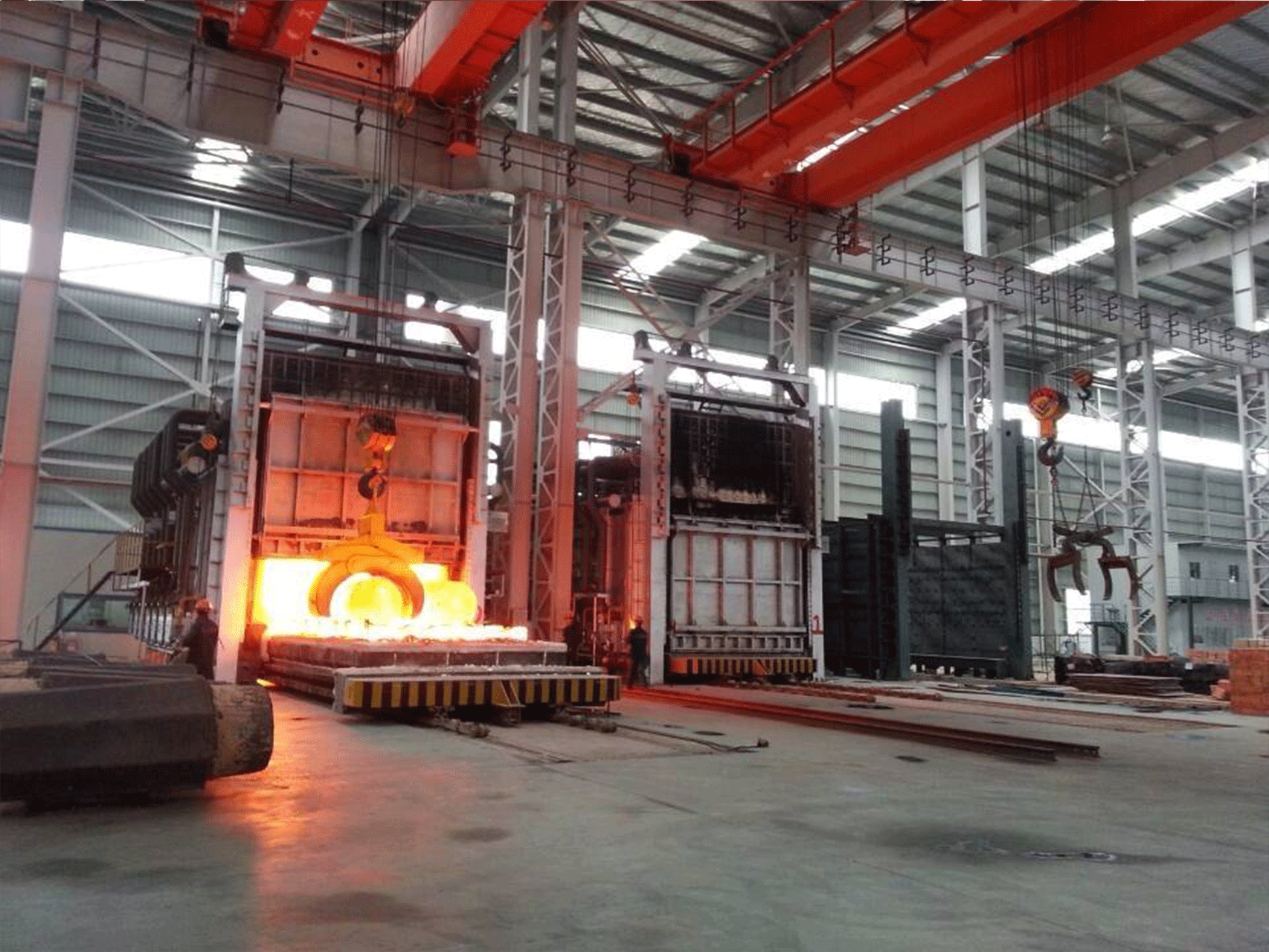
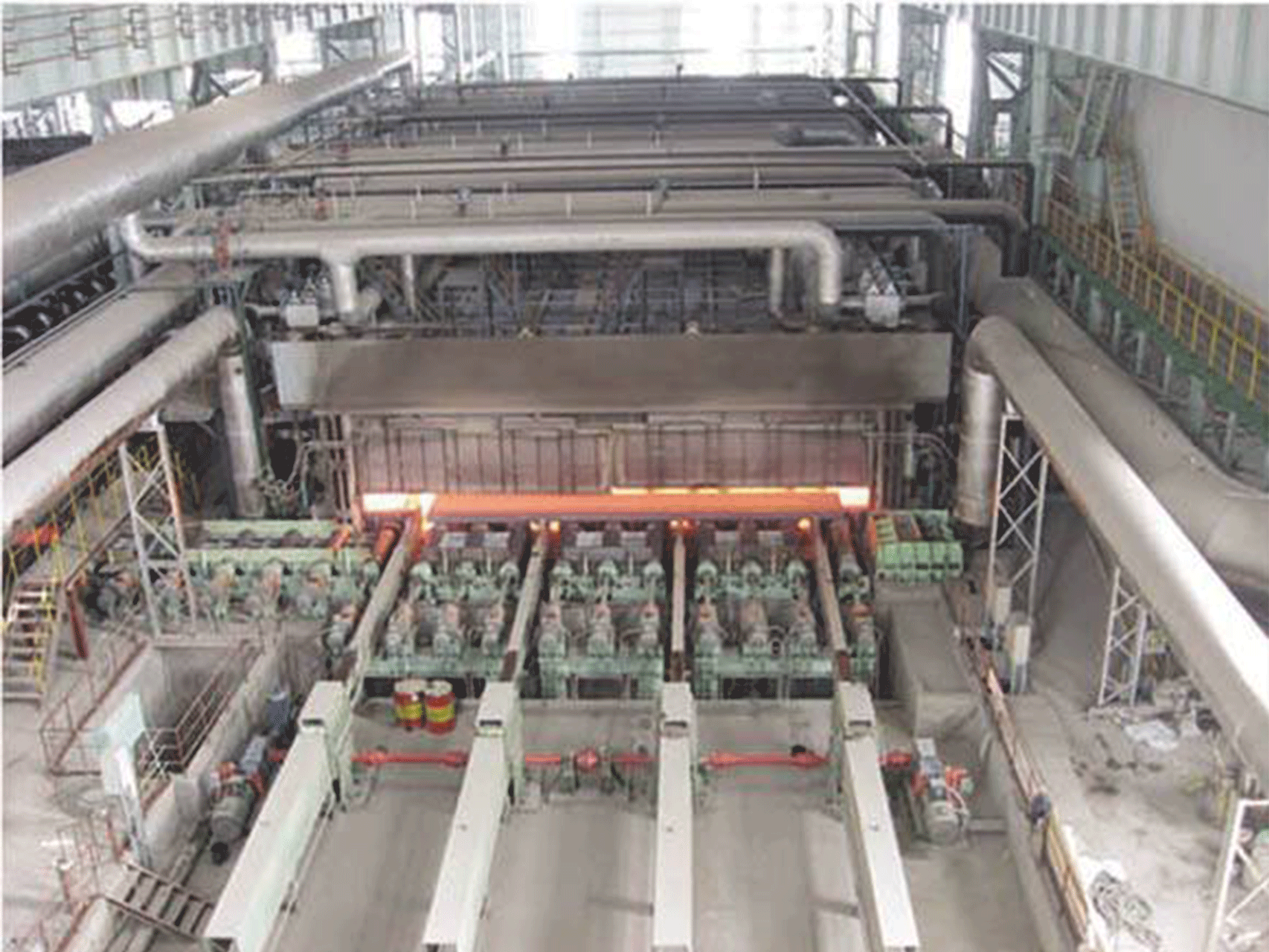
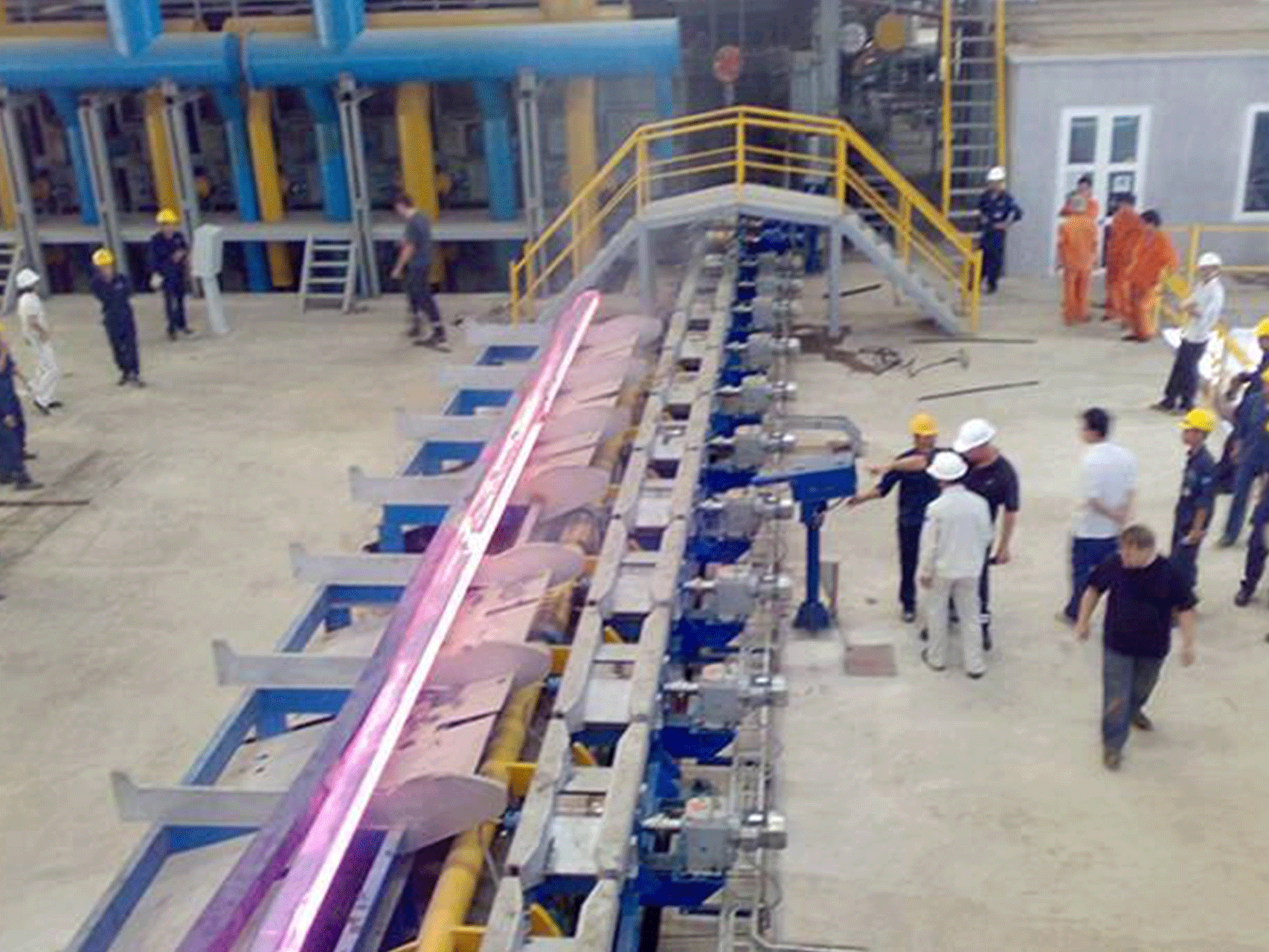
Reheating furnace for rolling mill
A reheating furnace is a type of furnace used in rolling mills to heat metal before it is shaped or rolled. It is an essential part of the rolling mill process as it allows the metal to be malleable and easier to work with, reducing the risk of damage or cracking during the rolling process. Reheating furnaces are typically fueled by natural gas or fuel oil and can be designed as either walking-beam or pusher-type.
The reheating process involves heating the metal to a specific temperature, often between 1000-1250 degrees Celsius and then holding it at that temperature for some time to ensure that the metal is evenly heated throughout. This is typically done in batches, with the metal being loaded into the furnace on a conveyor system or other automated mechanism. Once the metal has been reheated, it can be rolled or shaped into the desired form.
One of the main advantages of a reheating furnace is that it can help to increase the efficiency and productivity of the rolling mill process. By preheating the metal before it is rolled, less energy is required to achieve the desired shape or thickness, which can reduce costs and increase throughput. Additionally, reheating furnaces can be designed with advanced automation and control systems, allowing for precise temperature control and improved safety.
Advantages of Reheating furnace for rolling mill
The advantages of a reheating furnace for rolling mill include:
- Improved efficiency: The use of a reheating furnace can improve the efficiency of the rolling process by providing a uniform and controlled temperature to the material, reducing the amount of energy needed for the rolling process.
- Increased production: Reheating furnaces can help increase the production capacity of a rolling mill by reducing the time required for heating the material.
- Better quality: A reheating furnace can improve the quality of the rolled material by ensuring a consistent temperature throughout the process, which can result in fewer defects and improved mechanical properties.
- Reduced operating costs: Reheating furnaces can help reduce operating costs by optimizing fuel consumption and minimizing heat losses.
- Versatility: Reheating furnaces can be designed to process a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, and copper, making them suitable for use in a range of rolling mill applications.
Reheating furnace for rolling mill FQA
Q: What is a reheating furnace for a rolling mill?
A: A reheating furnace for a rolling mill is a furnace that heats metal ingots or billets to a specific temperature to make them malleable and ready for further processing in a rolling mill. It is used in the hot rolling process to reheat steel slabs or billets before rolling them into thinner and longer pieces. The reheating furnace is an important part of the rolling mill process as it ensures that the metal is heated evenly and to the correct temperature for efficient rolling.
Q: What types of fuel are used in reheating furnaces for rolling mills?
A: Reheating furnaces for rolling mills can use a variety of fuels, including natural gas, oil, coal, and electricity. The choice of fuel depends on several factors, including availability, cost, and environmental regulations. Natural gas and electricity are the most common fuels used in modern reheating furnaces due to their efficiency and environmental friendliness. However, some older facilities may still use coal or oil-fired furnaces, which are less efficient and produce more emissions.
Q: What are the main components of a reheating furnace for a rolling mill?
A: The main components of a reheating furnace for a rolling mill typically include:
- Charging system: This is used to load the material to be reheated into the furnace.
- Heating system: This includes burners, radiant tubes, or electric heating elements, which are used to heat the material.
- Exhaust system: This is used to remove the combustion gases and other byproducts of the heating process.
- Temperature control system: This includes temperature sensors and controllers, which are used to regulate the temperature inside the furnace.
- Material handling system: This is used to transfer the heated material from the furnace to the rolling mill or other downstream processes.
- Refractory lining: This is a layer of high-temperature insulation that lines the inside of the furnace to protect the outer shell from heat damage and to retain heat inside the furnace.
- Burner management system: This includes safety devices, such as flame sensors and pressure switches, which are used to monitor the burners and shut off the fuel supply in case of a malfunction or safety issue.
Q: What is the temperature range of a reheating furnace for a rolling mill?
A: The temperature range of a reheating furnace for a rolling mill typically varies between 1000°C to 1300°C depending on the specific application and material being heated.
Q: How is the temperature controlled in a reheating furnace for a rolling mill?
A: The temperature in a reheating furnace for a rolling mill is controlled using temperature sensors that measure the temperature of the material being heated. The furnace is equipped with a control system that regulates the fuel and airflow to the furnace burners to maintain the desired temperature. Some reheating furnaces also use thermocouples or infrared sensors to monitor the temperature of the material being heated in real-time, which allows for more precise temperature control.
Q: What are some safety considerations when operating a reheating furnace for a rolling mill?
A: Several safety considerations need to be taken into account when operating a reheating furnace for a rolling mill. Some of the key considerations include:
- Fire hazards: Reheating furnaces operate at very high temperatures, which can create a significant risk of fire. It is important to have proper fire protection systems in place, such as sprinklers and fire alarms, and to follow strict safety protocols when handling fuels and other materials.
- Heat exposure: The high temperatures of a reheating furnace can also pose a risk of heat exposure to operators and maintenance personnel. Appropriate protective gear, such as heat-resistant clothing and gloves, should be worn when working around the furnace.
- Combustion hazards: Reheating furnaces use combustion to generate heat, which can create a risk of explosions and other hazards if not properly controlled. Regular maintenance and inspection of the furnace and associated equipment is essential to ensure safe and effective operation.
- Electrical hazards: Reheating furnaces often use high-voltage electrical systems to control temperature and other parameters. Proper grounding and insulation are critical to prevent electrical shock and other hazards.
- Material handling: The process of loading and unloading materials from the furnace can also pose safety risks, particularly if heavy or awkwardly shaped materials are involved. Proper lifting and handling equipment should be used, and operators should be properly trained in safe material handling procedures.