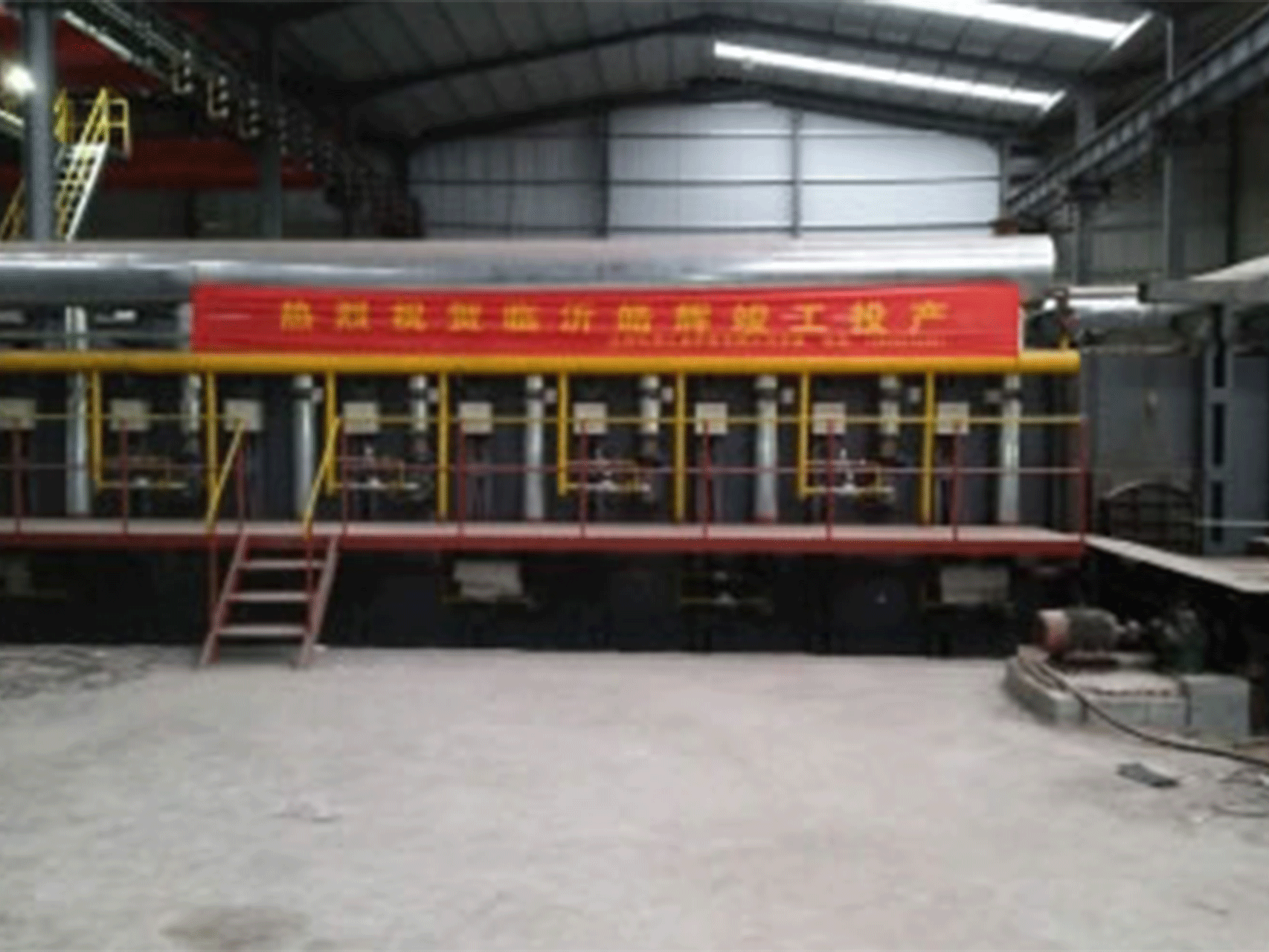
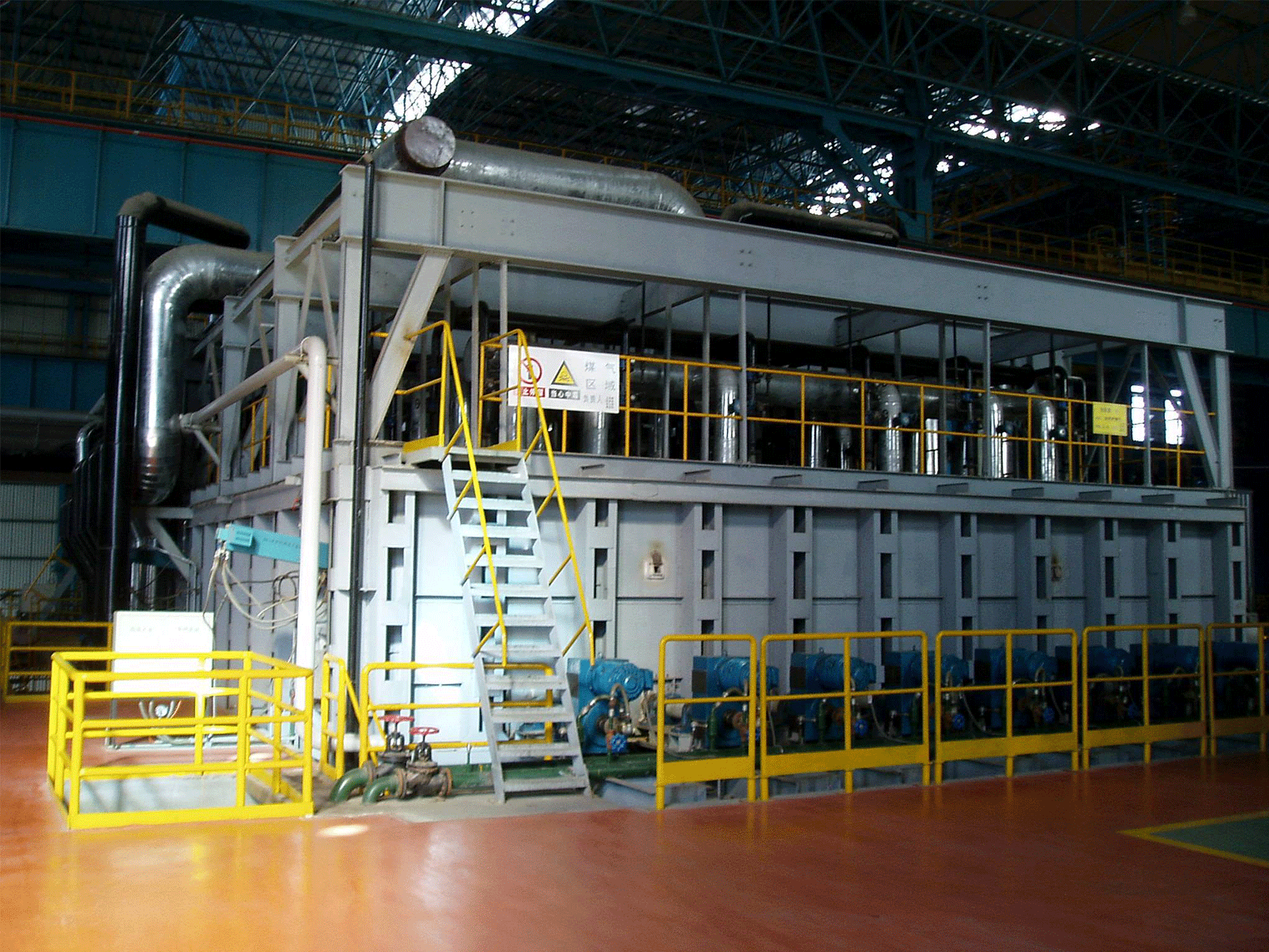
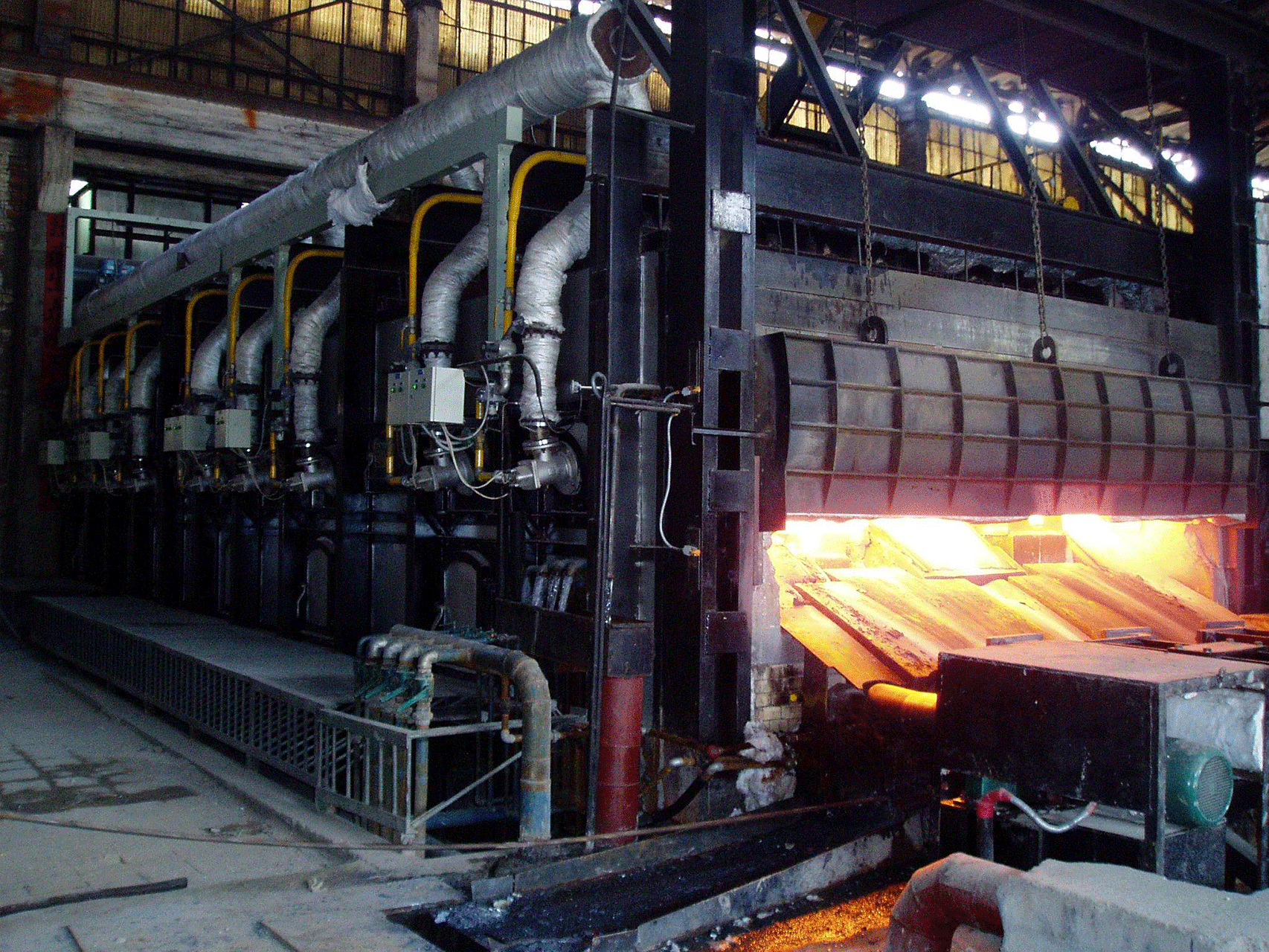
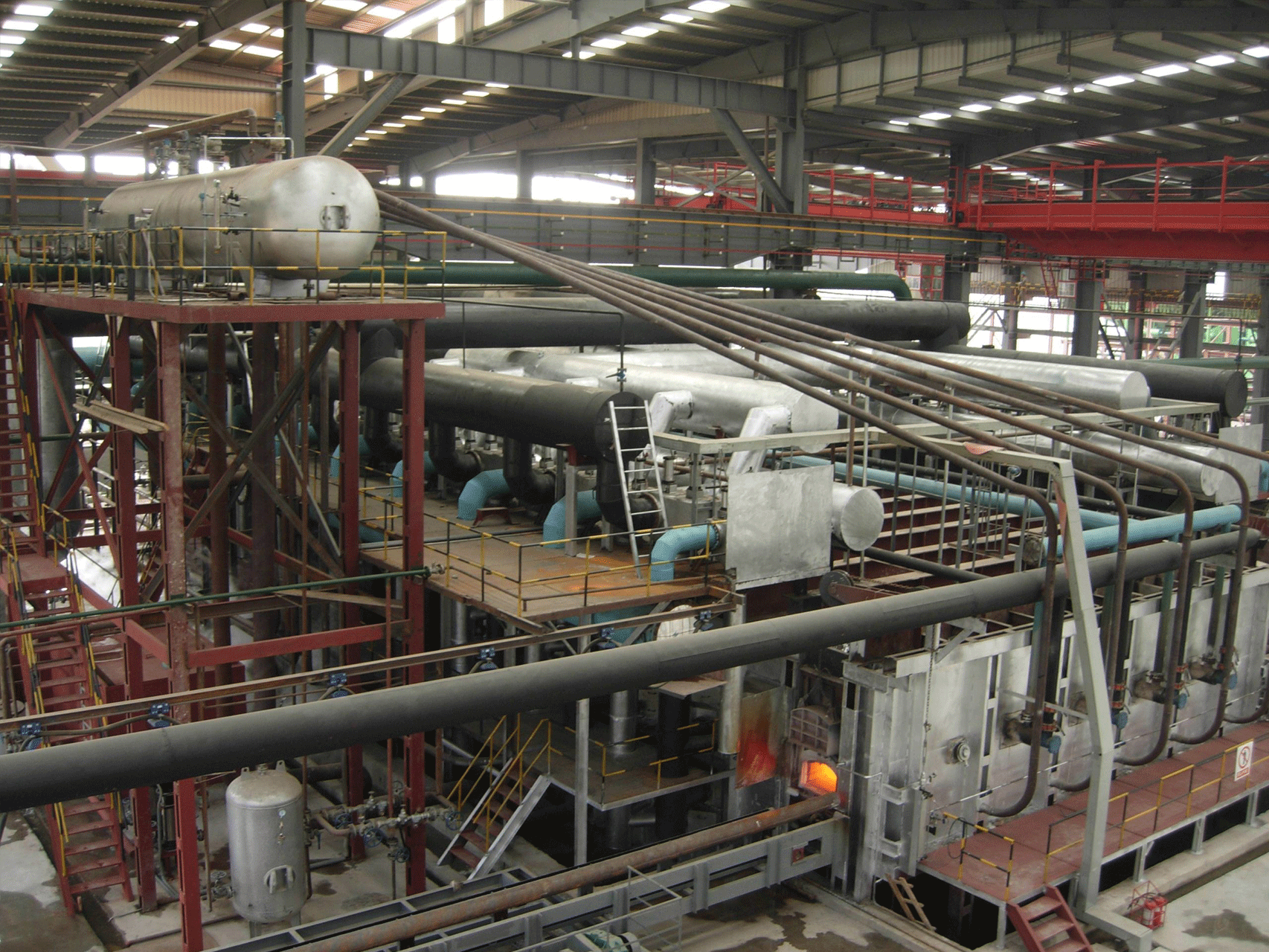
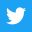
A rolling steel heating furnace is a type of industrial furnace that is used to heat steel in preparation for rolling or forging. The furnace is designed to bring the steel to a specific temperature range that allows it to be easily shaped and formed without cracking or breaking.
The heating process in a rolling steel furnace typically involves the use of natural gas or electricity as a fuel source. The steel is loaded into the furnace on a conveyor system, where it is heated to the desired temperature. The furnace is designed with a variety of heating elements and temperature sensors that allow for precise control over the heating process.
Once the steel has reached the desired temperature, it is removed from the furnace and sent to the rolling or forging process. The rolling process involves passing the heated steel through a series of rollers to shape it into the desired form, such as a sheet or a rod. The forging process consists in using a hammer or press to shape the heated steel into the desired form.
Rolling steel heating furnaces are commonly used in the steel and metalworking industries to produce a wide range of products, including automotive parts, construction materials, and consumer goods. They are designed to be highly efficient, reliable, and safe, with a variety of safety features and controls to ensure that the heating process is carried out safely and efficiently.
Working principle: rolling steel heating furnace
The working principle of a rolling steel heating furnace is based on the application of heat energy to a metallic material, such as steel, to raise its temperature to a specific range suitable for further processing. This is achieved through a heating system, which can be powered by electricity, natural gas, or other fuels.
The furnace typically consists of a refractory-lined chamber that houses the heating system, along with a conveyor system for loading and unloading the steel. The heating system can include burners, heating elements, or other sources of heat, depending on the type of furnace.
The steel is loaded onto the conveyor system and enters the furnace, where it is exposed to the heat energy produced by the heating system. The temperature of the furnace is carefully controlled to ensure that the steel is heated to the desired temperature range, which can vary depending on the type of steel and the processing requirements
Once the steel has been heated to the desired temperature, it is removed from the furnace and sent to the rolling or forging process, where it can be shaped and formed into the desired product.
Throughout the heating process, the furnace is equipped with various safety features and controls to ensure that the process is carried out safely and efficiently. These can include temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and other monitoring systems to detect any abnormalities or malfunctions that could compromise the safety or quality of the process
The characteristics
Some of the key characteristics of these furnaces include:
- High heating efficiency: Rolling steel heating furnaces are designed to be highly efficient, with a variety of heating elements and temperature controls that help to ensure that the heat energy is applied evenly and effectively to the steel. This helps to reduce energy consumption and minimize operating costs.
- Precise temperature control: These furnaces are equipped with advanced temperature sensors and control systems that allow for precise control over the heating process. This is essential for ensuring that the steel is heated to the correct temperature range, which can vary depending on the type of steel and the processing requirements
- Safety features: Rolling steel heating furnaces are designed with a variety of safety features and controls to ensure that the process is carried out safely and efficiently. These can include temperature and pressure sensors, emergency shut-off switches, and other monitoring systems that detect any abnormalities or malfunctions in the process.
- Versatility: These furnaces are highly versatile and can be used to heat a wide range of steel products, including sheets, rods, and other shapes. They can also be adapted to work with different types of fuels, such as natural gas, propane, or electricity, depending on the specific requirements of the