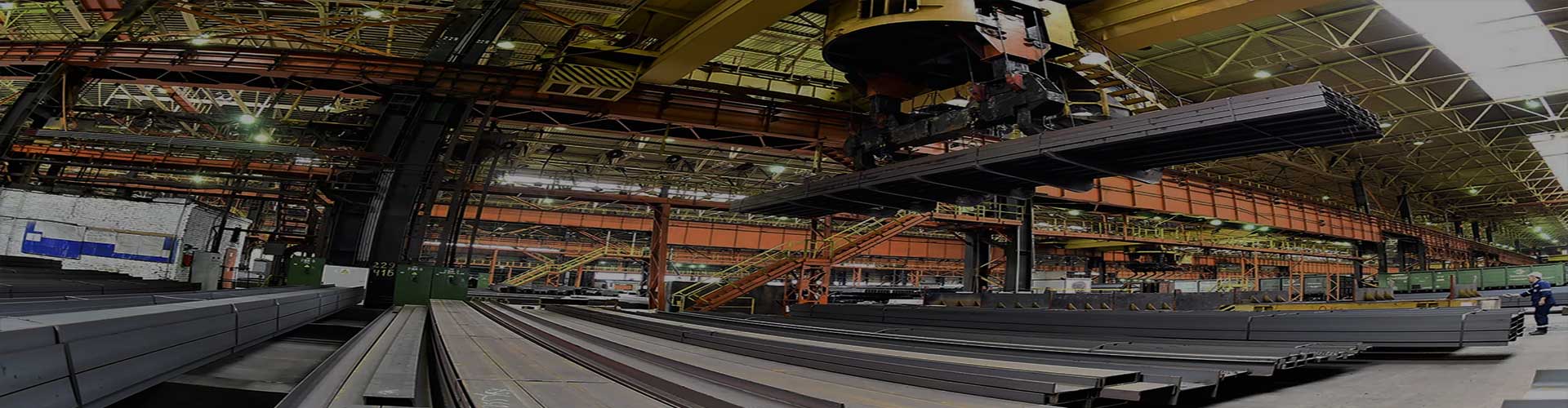
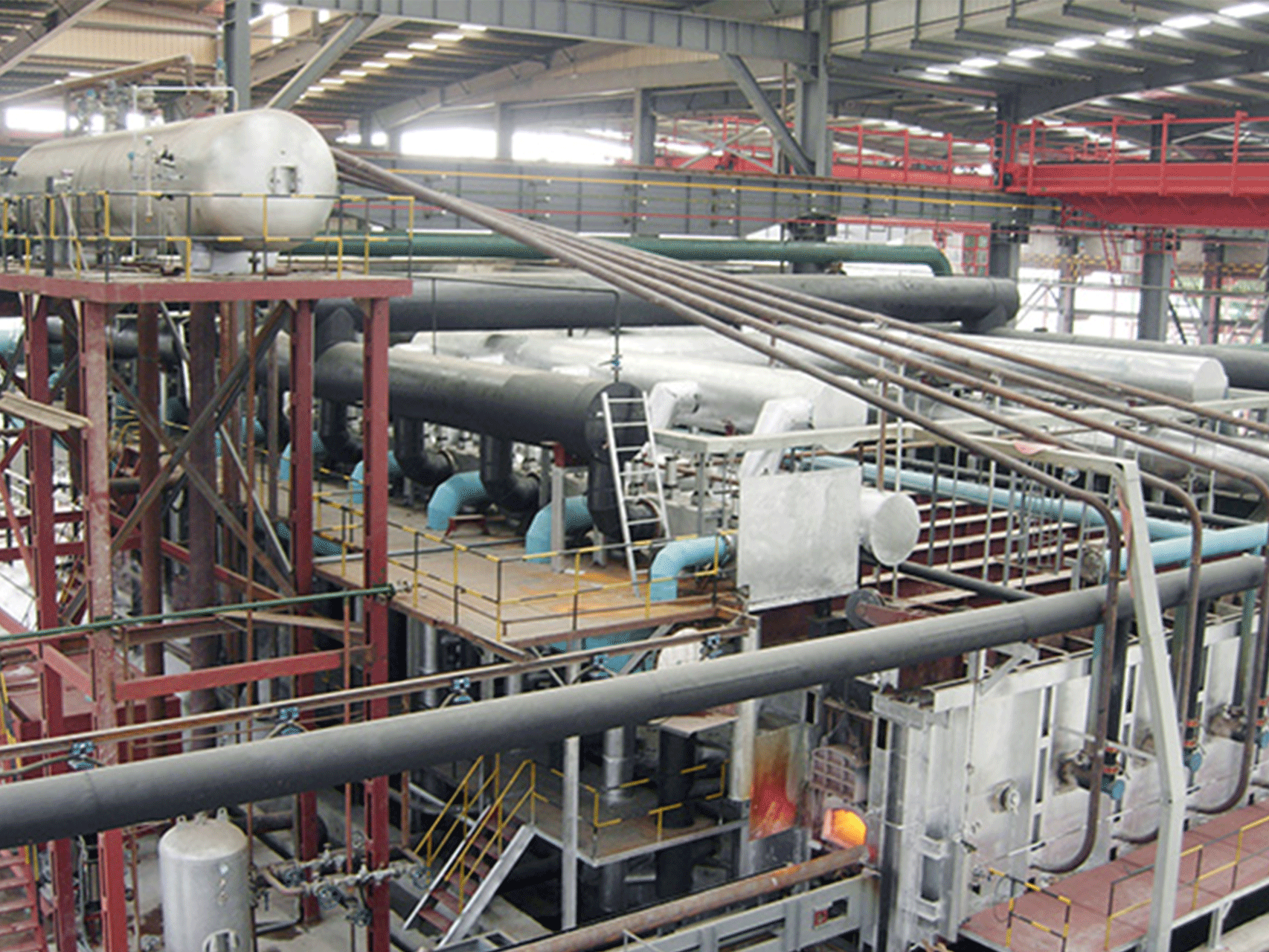
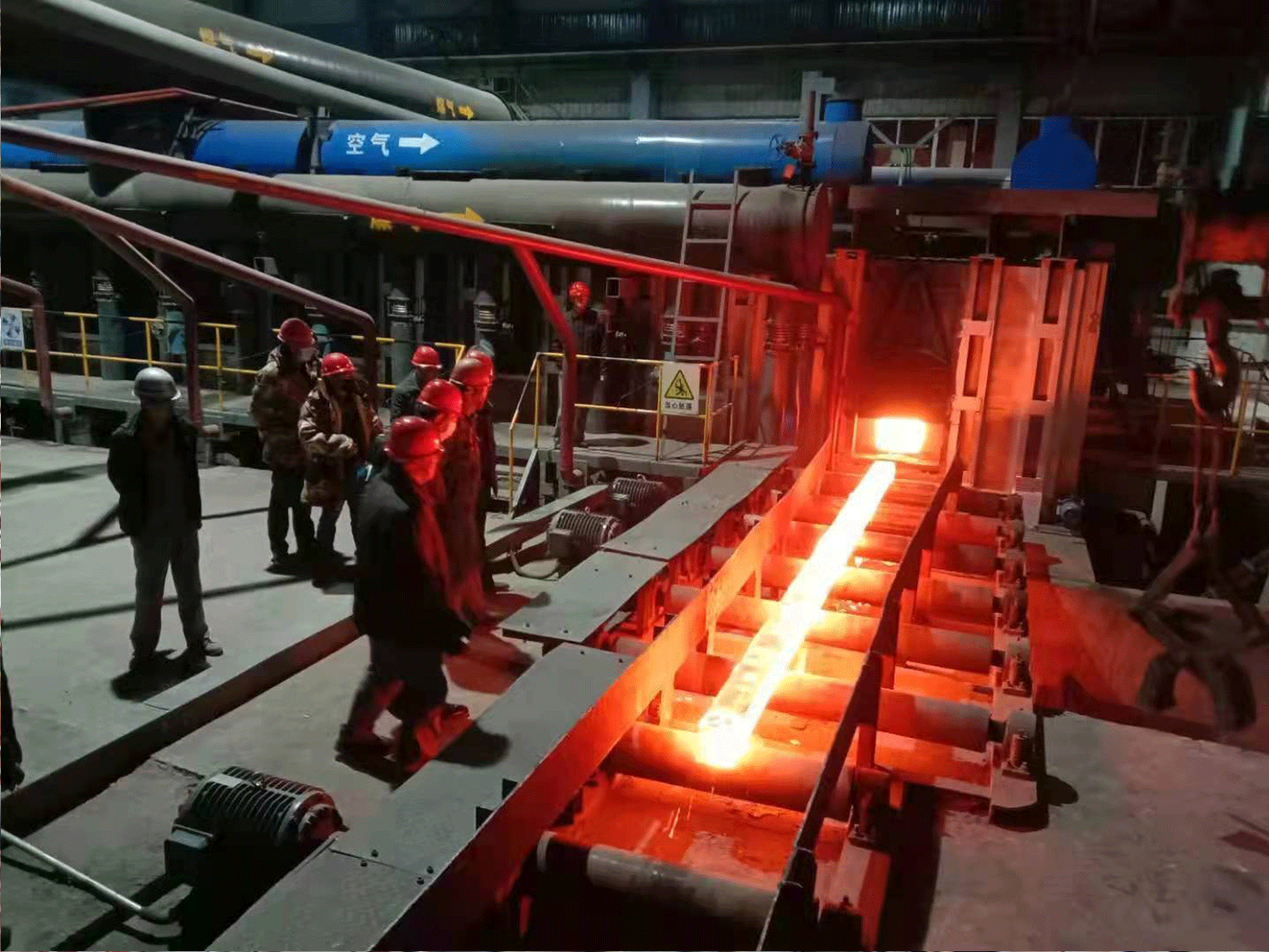
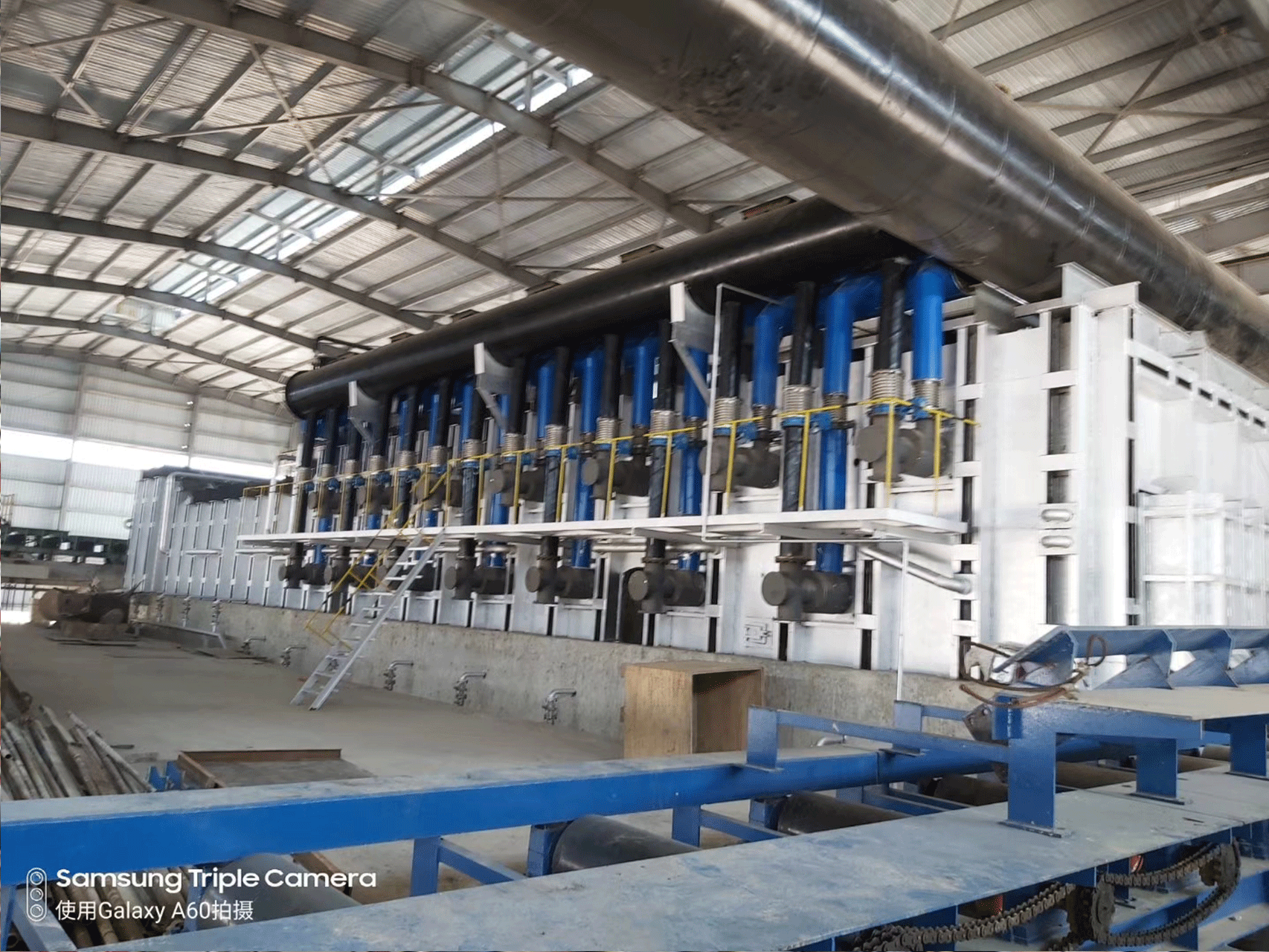
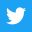
A Rolling Steel Heating Furnace is an industrial furnace used to heat steel billets or slabs prior to rolling them into finished products such as sheets, bars, or plates. The furnace operates in a continuous manner, with the steel being fed into one end of the furnace and transported through it on a conveyor system while it is being heated.
The furnace typically has multiple heating zones, each with its own heating source and temperature control system, which ensures that the steel is heated to the precise temperature required for rolling. The heating sources used can include natural gas, electricity, or other fuels.
The Rolling Steel Heating Furnace is an important component of the steel manufacturing process, as it helps to ensure that the finished products meet the required specifications for strength, durability, and other properties. It also enables large volumes of steel to be processed quickly and consistently, which helps to improve productivity and reduce production costs.
Rolling Steel Heating Furnace: Working Principle
A Rolling Steel Heating Furnace is a type of industrial furnace used in the steel industry to heat steel ingots or billets prior to rolling them into finished products. The working principles of this type of furnace involve a process of controlled heating that occurs within a closed chamber.
The following are the working principles of a Rolling Steel Heating Furnace:
- Loading the Furnace: The furnace is loaded with steel ingots or billets that are placed on rollers or conveyors that move them through the furnace chamber.
- Combustion: The furnace is heated by a burner system that uses either natural gas, propane, or fuel oil to produce a flame. The flame heats the air inside the furnace, which in turn heats the steel ingots or billets.
- Temperature Control: The temperature inside the furnace is controlled using thermocouples or pyrometers. These devices measure the temperature of the steel and adjust the burner system to maintain the desired temperature.
- Rolling: After the steel ingots or billets have been heated to the desired temperature, they are removed from the furnace and rolled into finished products using a rolling mill.
- Cooling: Once the steel has been rolled, it is cooled to prevent it from becoming too brittle. This can be done using water or air cooling systems.
Overall, the Rolling Steel Heating Furnace is an important component of the steel industry, as it allows for controlled heating of steel ingots and billets prior to rolling them into finished products.
The characteristics
The following are the characteristics of a Rolling Steel Heating Furnace:
- High Capacity: Rolling Steel Heating Furnaces are designed to handle large quantities of steel ingots and billets, typically up to several tons at a time.
- Fast Heating: Rolling Steel Heating Furnaces are designed to quickly and efficiently heat steel ingots and billets to the desired temperature, reducing cycle times and increasing productivity.
- Durability: Rolling Steel Heating Furnaces are built with heavy-duty materials, such as refractory bricks, to withstand the high temperatures and harsh operating conditions of the steel industry.
- Safety Features: Rolling Steel Heating Furnaces are equipped with safety features, such as flame sensors and over-temperature alarms, to ensure safe and reliable operation.
- Easy Maintenance: Rolling Steel Heating Furnaces are designed with easy access to critical components, such as the burner system and refractory lining, for routine maintenance and repair.
- Closed Chamber Design: The furnace chamber is designed to be completely enclosed to prevent heat loss and to ensure uniform heating of the steel.
- High-Temperature Capability: Rolling Steel Heating Furnaces are designed to operate at high temperatures, typically between 1000°C and 1300°C, to efficiently heat steel ingots and billets.