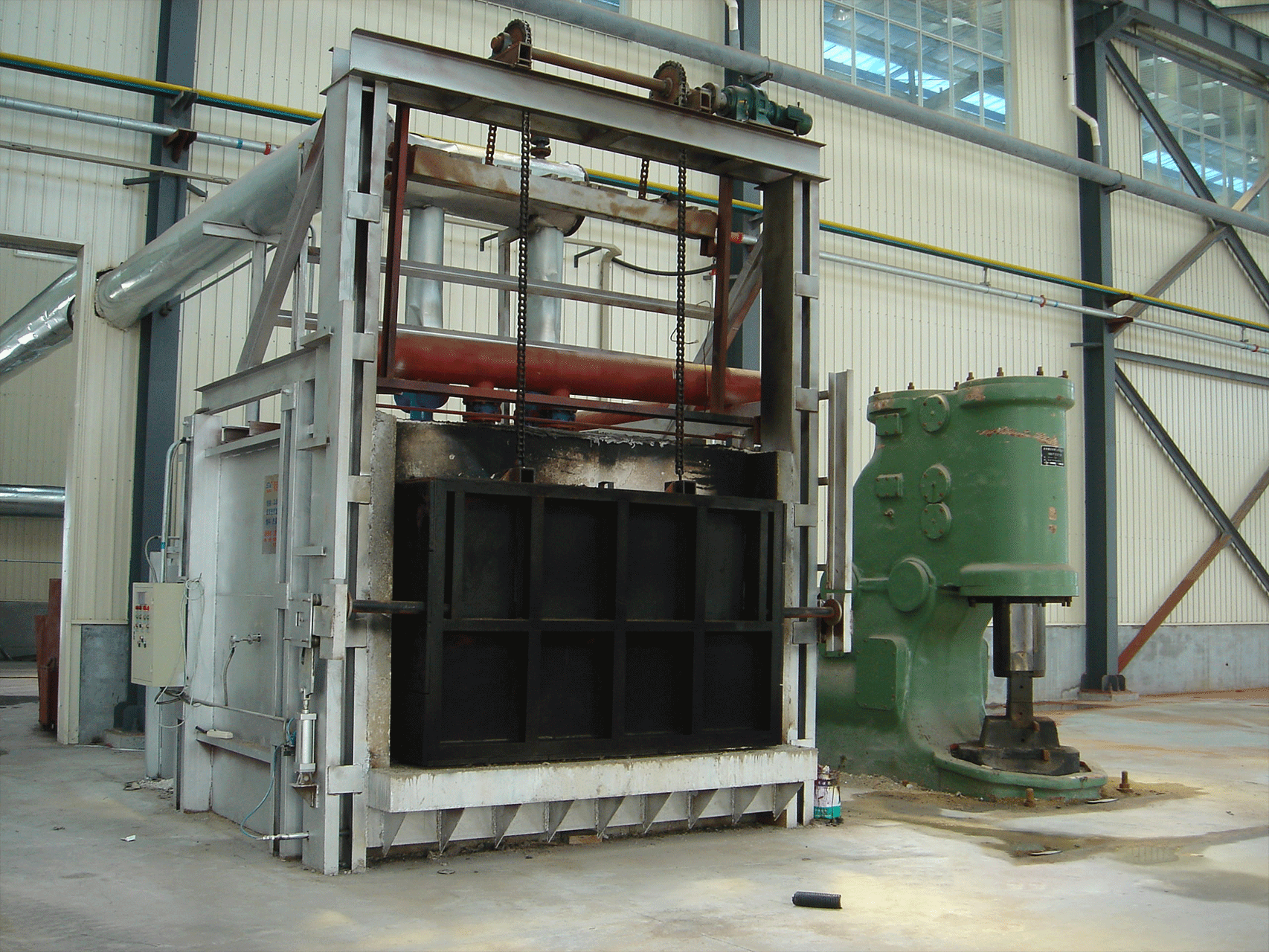
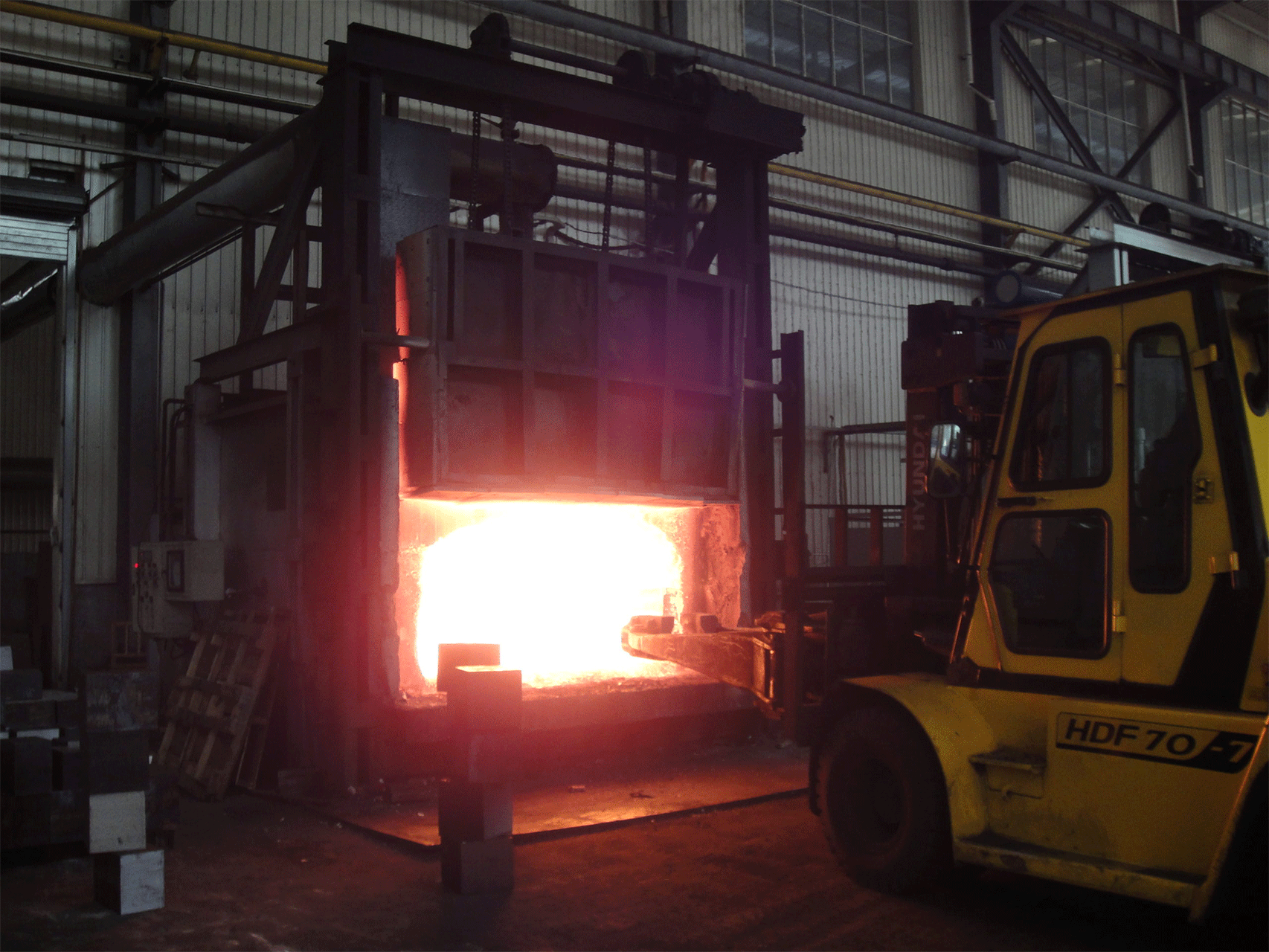
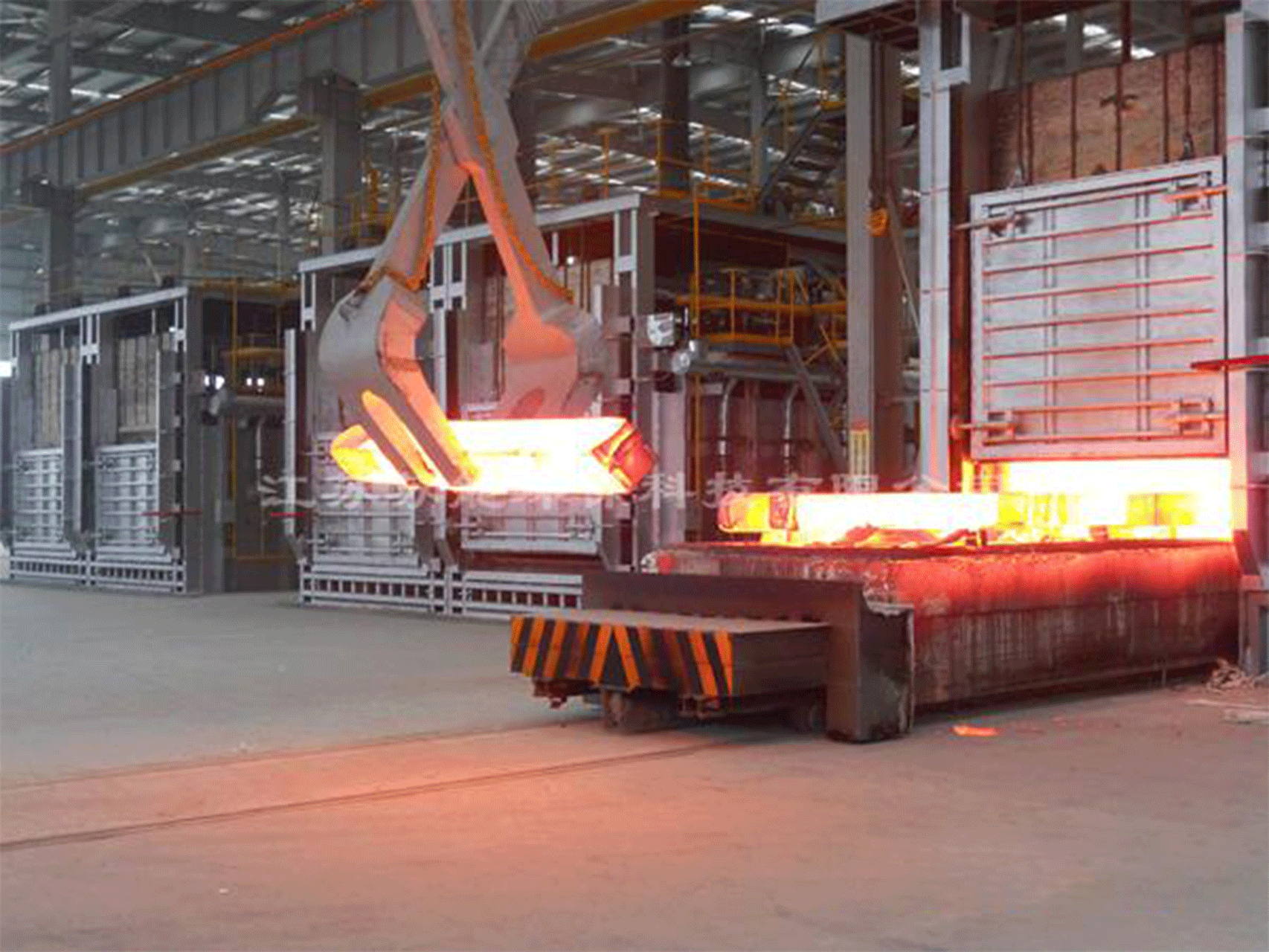
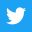
A regenerative gas-fired forging furnace is a type of industrial furnace that uses natural gas as a fuel source and employs a regenerative heat recovery system to improve its efficiency. This type of furnace is typically used in metalworking industries, such as forging and heat treating.
The furnace works by burning natural gas in a combustion chamber, which generates heat. The heat is then transferred to the forging material through the furnace walls and floor. However, in a regenerative gas-fired forging furnace, the waste heat is recovered and used to preheat the incoming combustion air, thereby increasing the efficiency of the furnace.
The furnace uses two chambers, one for combustion and one for preheating. The chambers alternate roles in a cycle, with the preheating chamber becoming the combustion chamber and vice versa. This allows for the efficient recovery and reuse of the waste heat.
Regenerative gas-fired forging furnaces are capable of reaching high temperatures quickly and maintaining a consistent temperature, making them ideal for use in industrial forging processes.
Working principle: regenerative gas-fired forging furnace
A regenerative gas-fired forging furnace works by using burners to heat the air and fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. The hot gases produced by the combustion process are then passed through a ceramic heat exchanger, which absorbs the heat and transfers it to the incoming air and fuel mixture. This preheating of the air and fuel mixture allows for more efficient combustion and reduces fuel consumption.
The heat exchanger in a regenerative furnace is designed with two chambers, one for heating and one for cooling. The hot gases flow through the heating chamber, and the cooled gases flow through the cooling chamber, which is filled with a material such as ceramic bricks or honeycomb structures that can absorb and store heat.
After a set period, the flow of hot gases is reversed, and the cool gases are redirected to the heating chamber, while the hot gases are directed to the cooling chamber. This process allows the heat exchanger to be continuously regenerated, and the furnace can maintain a constant temperature without requiring excessive amounts of fuel.
In addition to the heat exchanger, a regenerative furnace may also have a combustion control system that monitors the temperature and oxygen levels in the combustion chamber and adjusts the fuel and air mixture to maintain optimal combustion efficiency.
The Characteristics
The main characteristics of a regenerative gas-fired forging furnace include:
- High energy efficiency: The regenerative furnace can recover a significant amount of the heat generated during the combustion process, reducing energy consumption and fuel costs.
- Consistent temperature control: The regenerative furnace can maintain a constant temperature due to its efficient heat transfer and combustion control systems, resulting in consistent forging results.
- Low emissions: The regenerative furnace can reduce emissions due to its efficient combustion process, resulting in a cleaner and safer working environment.
- Low maintenance: The regenerative furnace requires less maintenance compared to traditional furnaces, as the heat exchanger is made from durable materials and does not require frequent replacements.
- Flexible operations: The regenerative furnace can be operated with different types of gases, such as natural gas, propane, or butane, providing flexibility in operations.
- Fast heating: The regenerative furnace can heat up quickly, reducing the overall forging cycle time and increasing production efficiency.
| Item | Consumption value | Remarks | |
| Natural gas | 350Nm3/h | Heat value: 8900Kcal/Nm3 8900Kcal/Nm3 |
|
| Cycle water | 12m3/h | ||
| Soft water | 4 m3/h | ||
| Electric | 5KWh/t | ||
| Nitrogen | 12 Nm3/time 12 Nm3/ |
||
| Compressed air | 0.2 Nm3/time 0.2 Nm3/ |