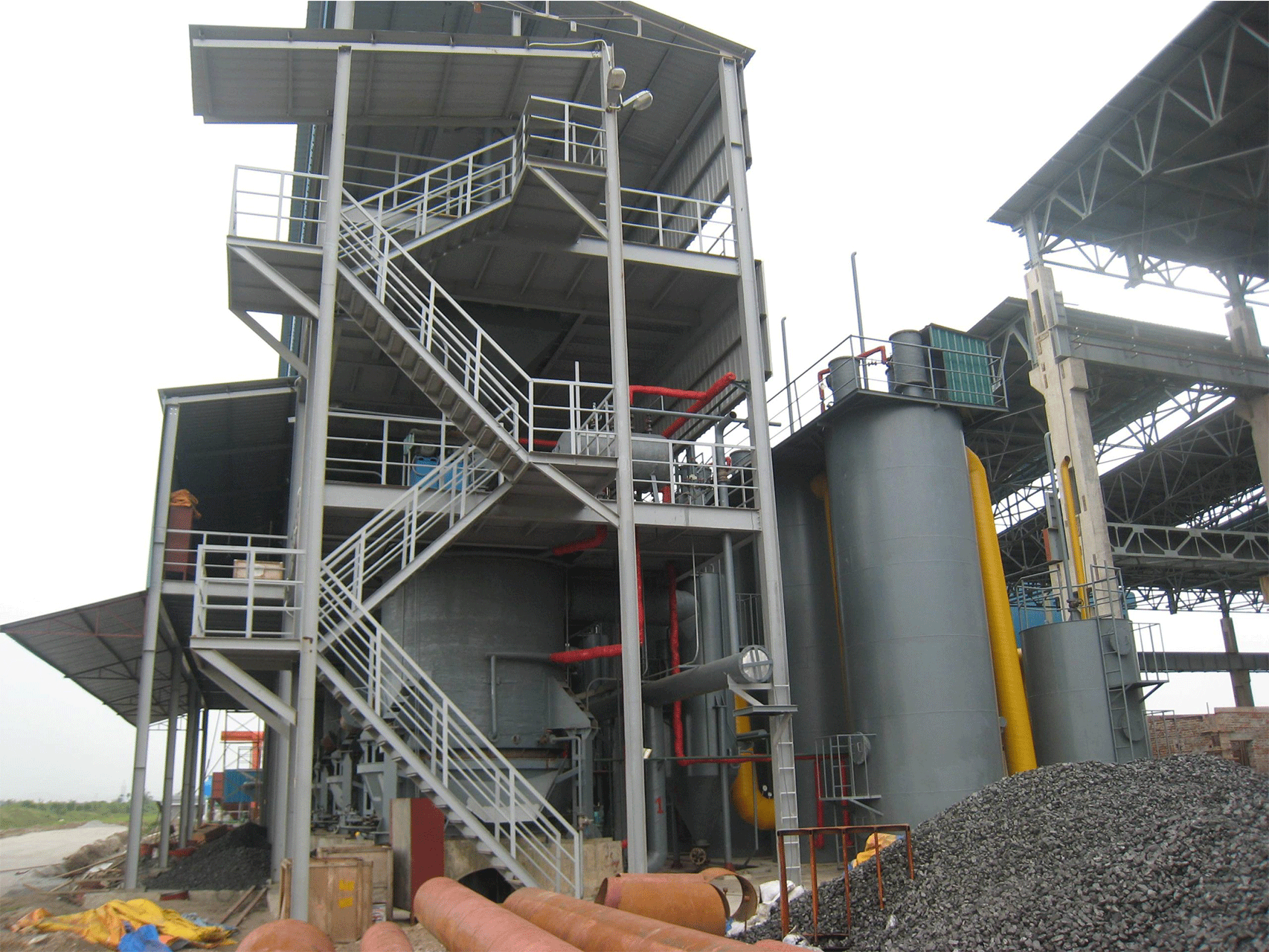
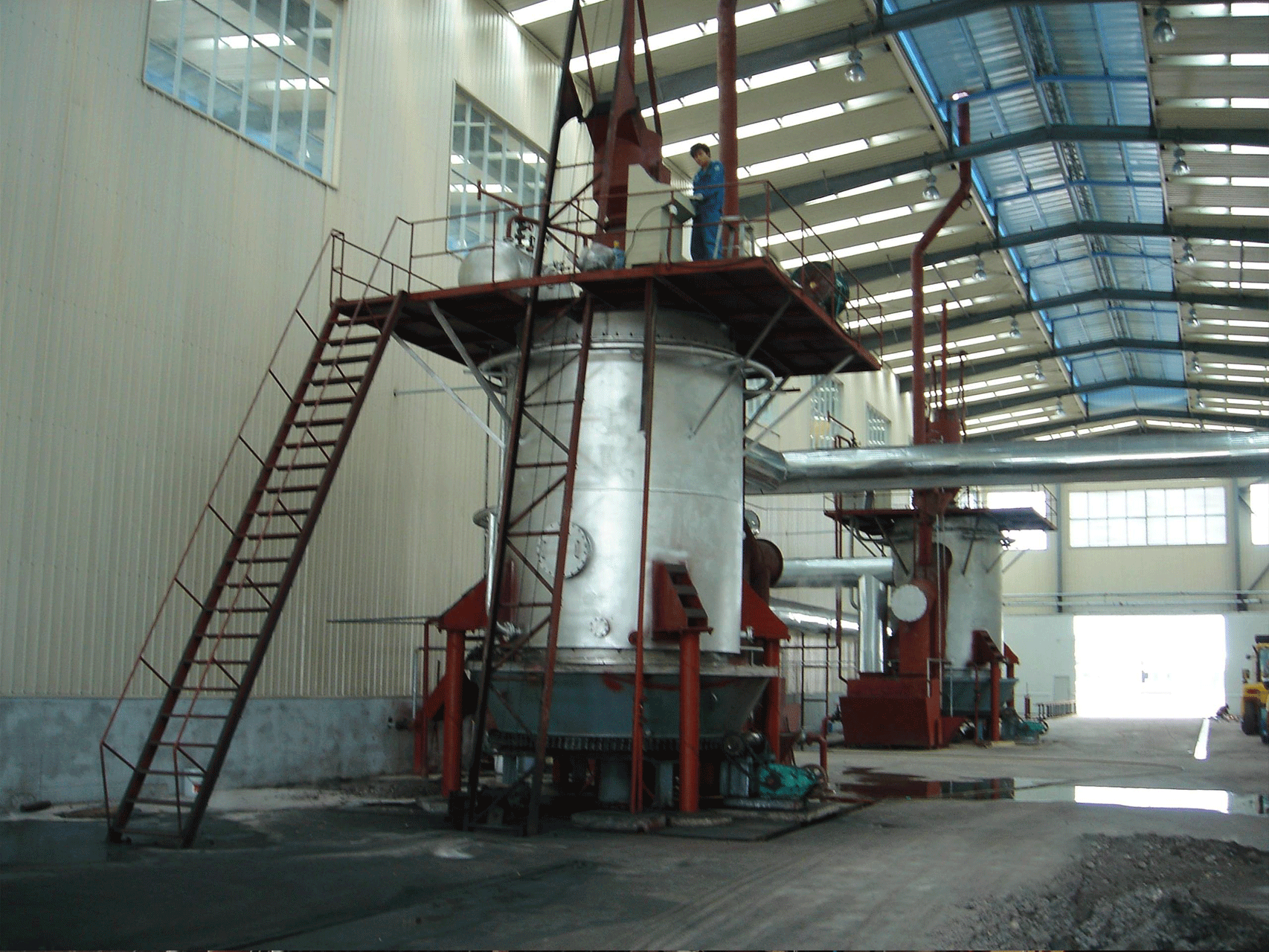
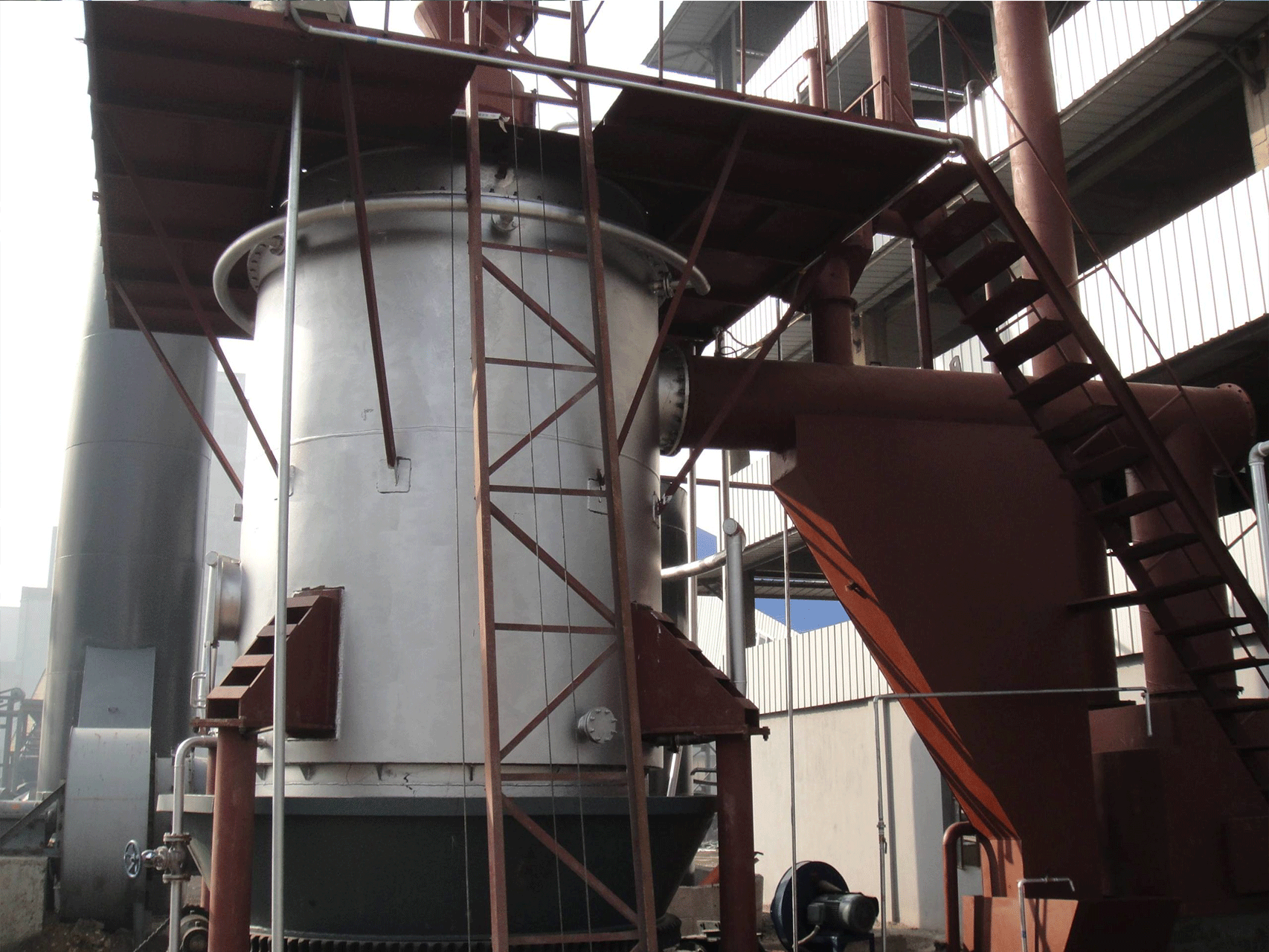
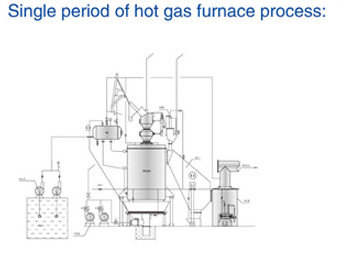
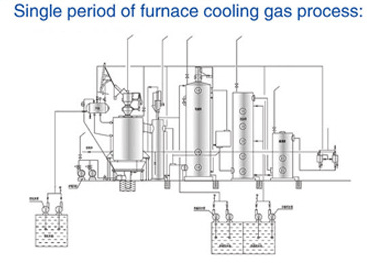
A coal gasifier is a device that converts coal into a gas called “syngas” through a process known as gasification. Gasification involves exposing coal to high temperatures and controlled amounts of oxygen or steam to break down the coal into its parts, including carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane.
The syngas produced by the coal gasifier can be used for a variety of purposes, including generating electricity, producing synthetic fuels, and manufacturing chemicals. The process of gasification is considered to be more efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional coal-burning power plants, as it produces fewer emissions and can also utilize low-grade or waste coal.
However, gasification technology is still relatively new and has some challenges that need to be addressed, such as the high cost of building and operating gasification plants, as well as the need to find cost-effective ways to capture and store the carbon dioxide produced by the process. Nevertheless, gasification is considered to be a promising technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the use of coal and other fossil fuels.
Coal gasifier: working principle
The working principle of a coal gasifier involves several steps:
- Coal is fed into the gasifier from the top, and it falls into a bed of hot, inert material, such as sand or coke.
- A controlled amount of oxygen and steam is injected into the gasifier from the bottom, where it reacts with the coal in the bed. The chemical reactions that take place are: C + O2 -> CO2
- C + H2O -> CO + H2: These reactions produce carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen (H2), which are the main components of syngas.
- The syngas produced rise to the top of the gasifier, where it is cooled and cleaned. Any impurities, such as sulfur and ash, are removed from the syngas.
- The cleaned syngas is then used as a fuel for power generation or as a feedstock for chemical production.
Overall, the coal gasifier operates on the principle of partial combustion, where only a fraction of the coal is burned in the presence of a limited amount of oxygen and steam, producing syngas with lower emissions of pollutants than traditional coal combustion.
The characteristics
Some of the key characteristics of a coal gasifier include:
- High Temperatures: Coal gasification involves exposing coal to temperatures of around 700-1500 degrees Celsius. These high temperatures help to break down the coal into its parts and convert it into syngas.
- Controlled Oxygen or Steam Supply: The gasification process requires a controlled supply of oxygen or steam to regulate the chemical reactions taking place. This ensures that the coal is converted into syngas rather than being fully combusted.
- Syngas Production: The main product of the coal gasification process is syngas, which are composed of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and other gases. This syngas can be used to generate electricity, produce synthetic fuels, or as feedstock for chemical production.
- Lower Emissions: Compared to traditional coal-burning power plants, gasification produces fewer emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. This is because the gasification process is more efficient and allows for more complete combustion of the coal.
- Versatility: Syngas produced by a coal gasifier can be used for a variety of purposes, including generating electricity, producing synthetic fuels, and manufacturing chemicals. This versatility makes gasification a promising technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the use of coal and other fossil fuels.
Technology parameters:
Single-stage gas generator technical performance parameters
| Model | YDSQ1.0 | YDSQ1.5 | YDSQ2.0 | YDSQ2.4 | YDSQ2.6 | YDSQ3.0 | YDSQ3.2 |
| Type | CG1Q1.0-1 | CG1Q1.5-1 | CG1Q2.0-1 | CG1Q2.4-1 | CG1Q2.6-1 | CG1Q3.0-1 | CG1Q3.2-1 |
| Inner diameter of furnace chamber(mm) | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 2400 | 2600 | 3000 | 3200 |
| Cross-sectional area of furnace chamber(m²) | 0.785 | 1.77 | 3.14 | 4.52 | 5.31 | 7.07 | 8.04 |
| Height of fuel layer(mm) | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Height of fire layer(mm) | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 |
| Height of ash layer(mm) | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 | 100-300 |
| Heating area of water jacket(m²) | 6.84 | 10.09 | 20.06 | 27.16 | 31.51 | 32.4 | 31.35 |
| Applicable coal type | Unbonded or weakly bonded anthracite, bituminous coal or coking coal Coal quality should meet the requirements of GB-9143 | ||||||
| Coal size(mm) | 13-25 | 13-25、25-50 | |||||
| Coal consumption(kg/h) | 125-198 | 280-440 | 500-792 | 720-1144 | 850-1320 | 1130-1782 | 1280-2035 |
| Gasification agent | Air + water vapor | ||||||
| Air consumption(m³/kg coal) | 2.2-2.8 | 2.2-2.8 | 2.2-2.8 | 2.2-2.8 | 2.2-2.8 | 2.2-2.8 | 2.2-2.8 |
| Steam consumption(kg/kg coal) | 0.3-0.5 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.3-0.5 |
| Gas production(Nm²/h) | 450-715 | 980-1540 | 1750-2750 | 2500-3960 | 3000-4730 | 3950-6237 | 4480-7117 |
| Gas calorific value(kj/m³) | 5020-6060 | 5020-6060 | 5020-6060 | 5020-6060 | 5020-6060 | 5020-6060 | 5020-6060 |
| Gas outlet pressure(pa) | <950 | <980 | <980 | <980 | <1500 | <1500 | <1500 |
| Gas outlet temperature(℃) | 400-550 | 400-550 | 400-550 | 400-550 | 400-550 | 400-550 | 400-550 |
| Max. furnace bottom blast pressure(pa) | 2000 | 2450 | 3500 | 3500 | 4000 | 6000 | 6000 |
| Saturated air temperature(℃) | 50-65 | 50-65 | 50-65 | 50-65 | 50-65 | 50-65 | 50-65 |
| Probe hole steam seal pressure(kpa) | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 |
| Water jacket steam output(kg/h) | 150-200 | 250-300 | 300-350 | 450-500 | 450-500 | 500-600 | 500-650 |
| Water jacket steam pressure(kpa) | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 | <294 |
| Coal addition method | Bellows coal addition, mechanical coal addition | ||||||
| Maximum speed of ash tray(rh) | 2.87 | 2.76 | 2.23 | 2 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Power of ash tray drive motor(kw) | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Power of coal bucket lifting motor(kw) | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3 | 3 |
| Slag discharge form | Wet type, automatic slag discharge | ||||||