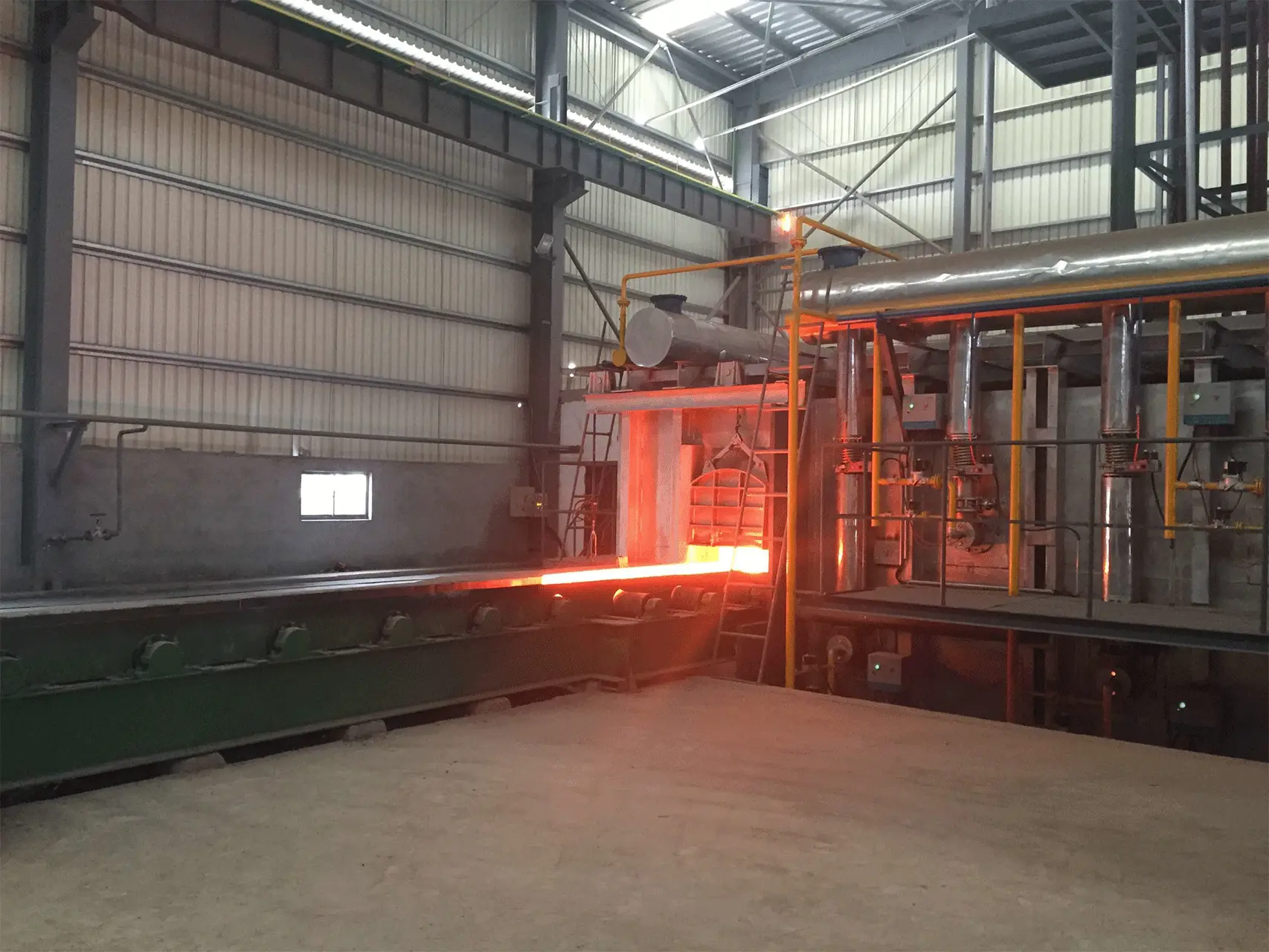
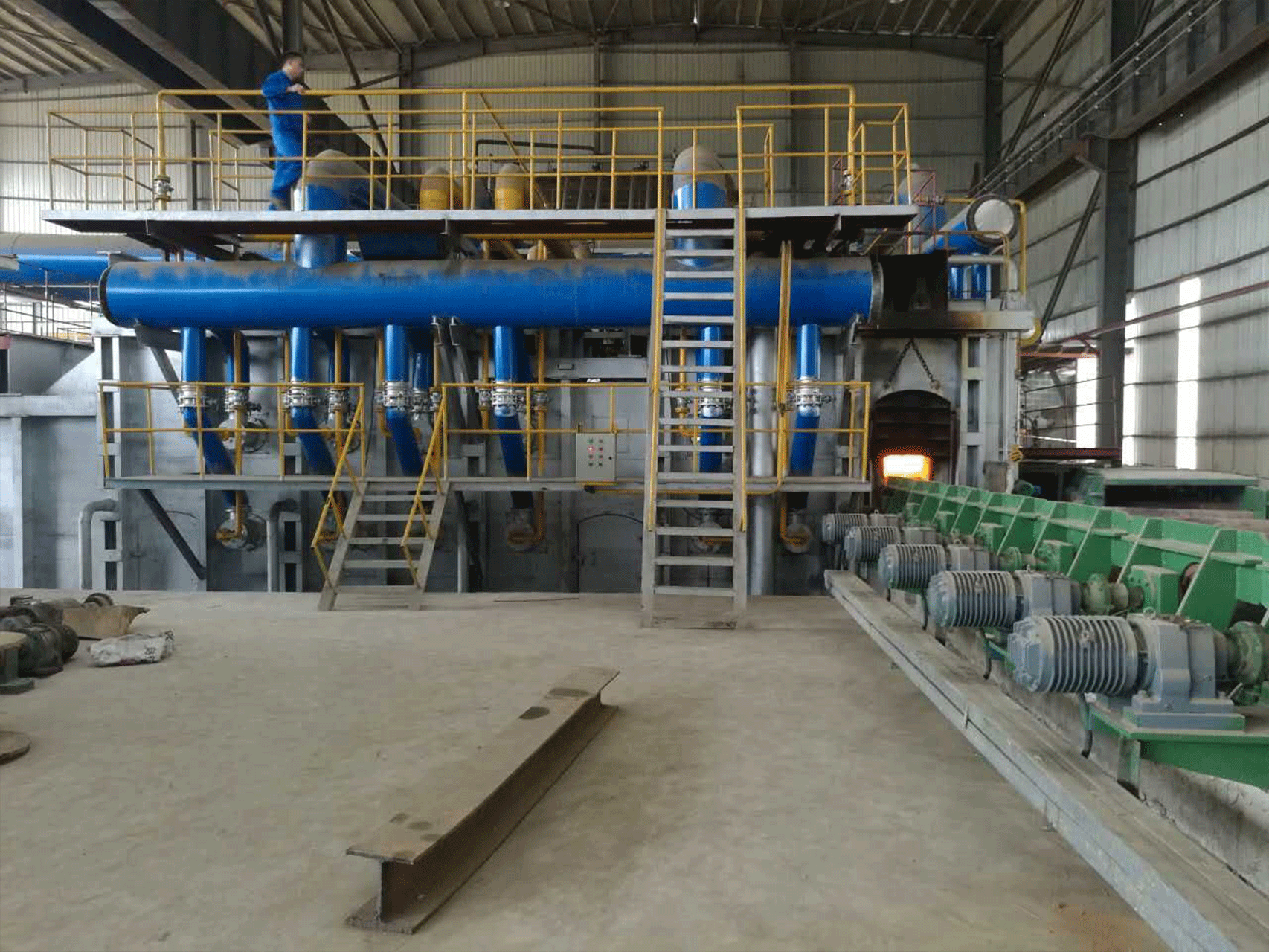
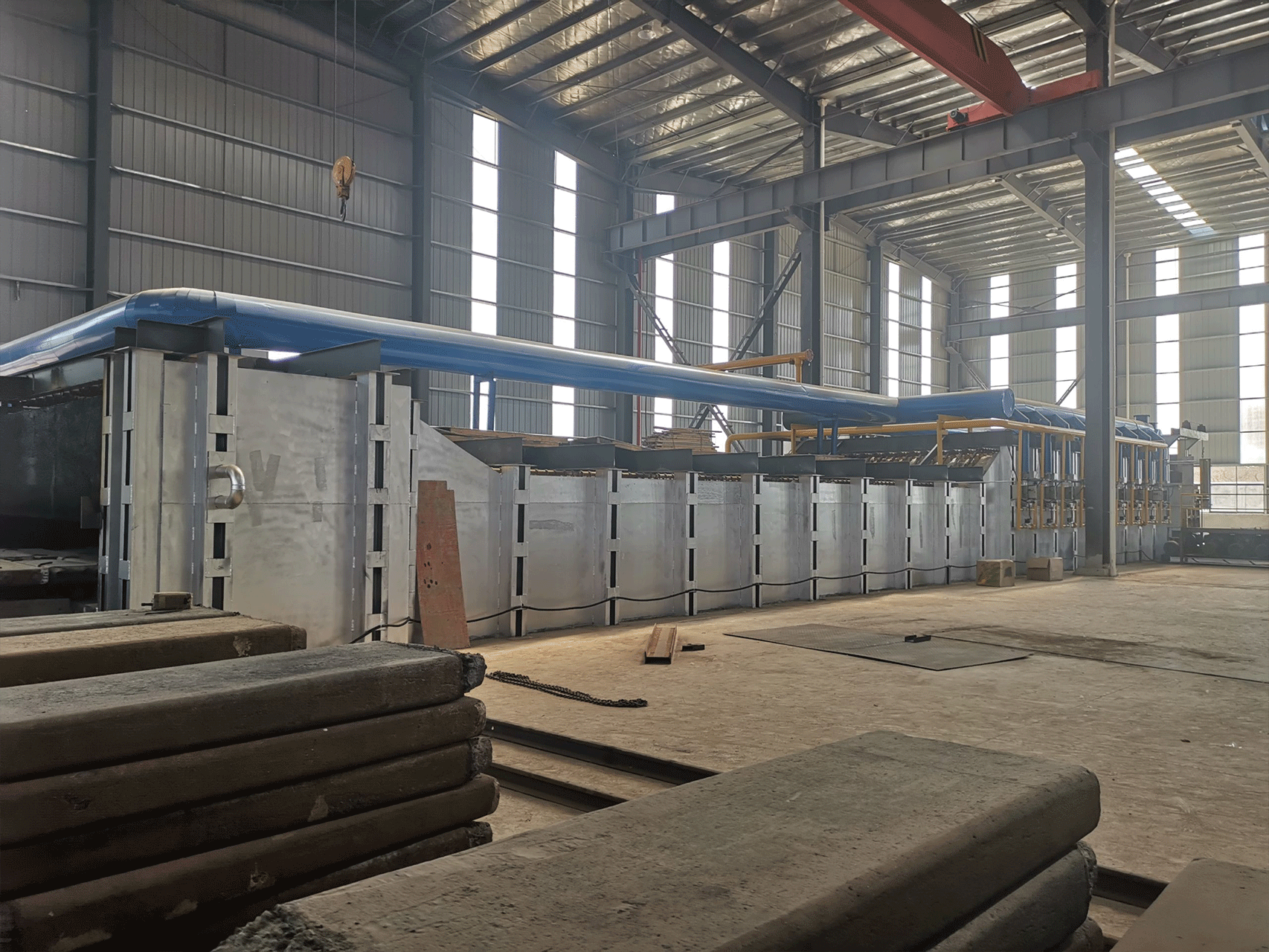
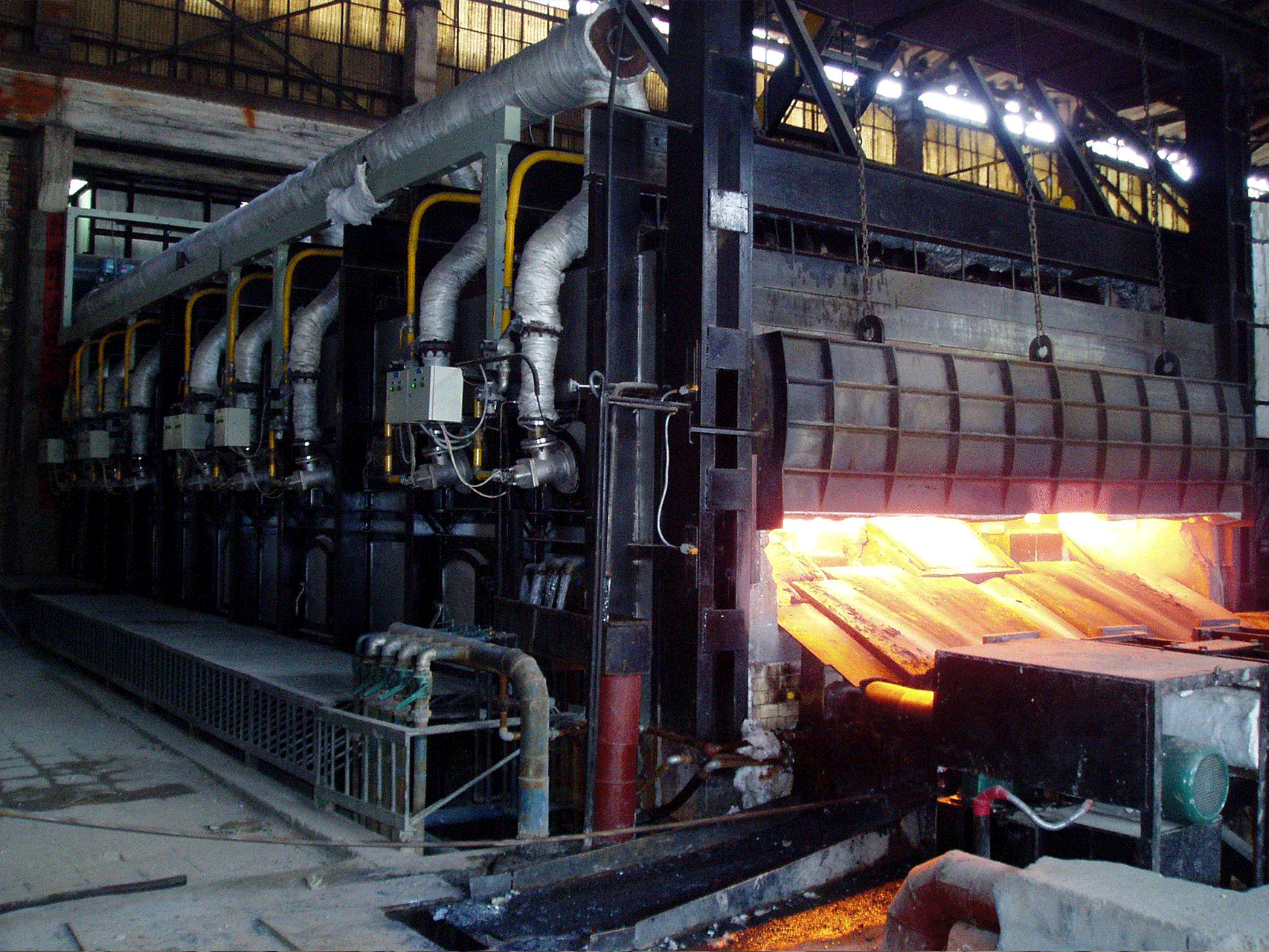
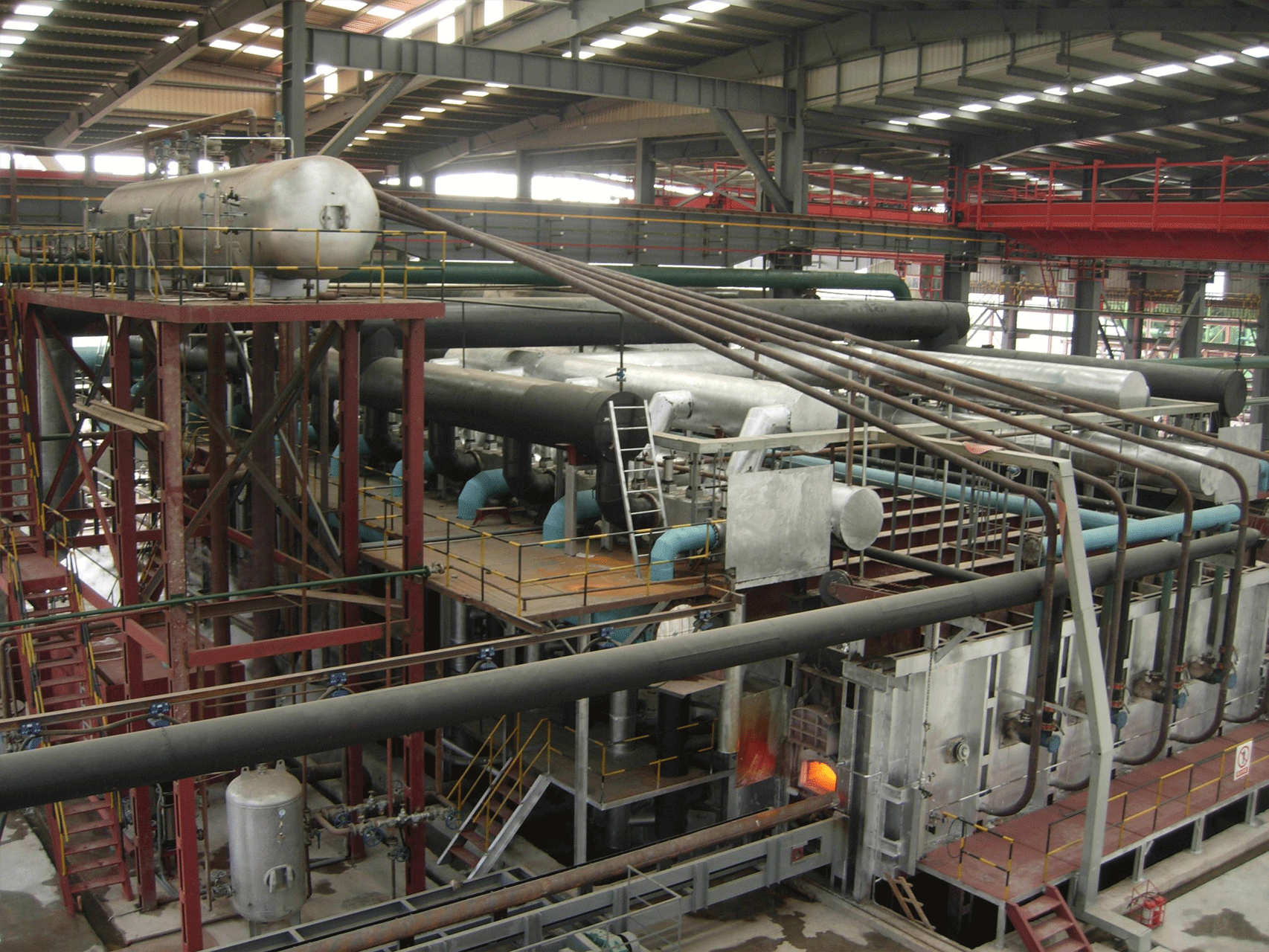
Continuous steel rolling heating furnaces are industrial furnaces used in the steel manufacturing process to heat steel billets or slabs before they are rolled into finished products such as sheets, bars, or plates. These furnaces are designed to operate continuously, with a conveyor system that feeds steel into the furnace at one end and transports it through the furnace to the other end, where it is ready for further processing.
The furnaces use various fuel sources, such as natural gas or electricity, to generate heat, which is directed onto the steel billets or slabs as they pass through the furnace. The heating process is carefully controlled to ensure that the steel is heated to the correct temperature for rolling and that the temperature is consistent throughout the entire billet or slab.
Continuous steel rolling heating furnaces are a critical component of the steel manufacturing process, as they play a key role in ensuring that the finished products meet the required specifications for strength, durability, and other properties. They are also important for ensuring that the production process is efficient and cost-effective, as they enable large volumes of steel to be processed quickly and consistently.
Continuous steel rolling heating furnaces : Working Principle
Continuous steel rolling heating furnaces work on the principle of heating steel billets or slabs to a precise temperature before they are rolled into finished products such as sheets, bars, or plates. The furnaces operate continuously, with a conveyor system that feeds steel into the furnace at one end and transports it through the furnace to the other end.
The heating process begins as the steel billets or slabs enter the furnace and move along the conveyor. The furnace is typically divided into multiple heating zones, each with its own heating source and temperature control system. As the steel moves through each heating zone, it is subjected to a carefully controlled temperature profile that heats it to the desired temperature for rolling.
The heating sources used in continuous steel rolling heating furnaces can vary depending on the specific furnace design and production requirements. Some furnaces use natural gas or other fuels to generate heat, while others use electric heating elements. In either case, the heat is directed onto the steel billets or slabs using a combination of radiant heat and convection.
The temperature control system in a continuous furnace is critical to ensuring that the steel is heated to the correct temperature for rolling and that the temperature is consistent throughout the entire billet or slab. The control system typically includes sensors that monitor the temperature of the steel as it moves through the furnace, as well as control algorithms that adjust the temperature of each heating zone to maintain the desired temperature profile.
Overall, continuous steel rolling heating furnaces are a critical component of the steel manufacturing process, as they enable large volumes of steel to be processed quickly and efficiently while ensuring consistent quality in the finished products.
The characteristic
Continuous steel rolling heating furnaces offer several benefits for the steel manufacturing process, including:
- Improved energy efficiency: Continuous furnaces are designed for maximum energy efficiency, with heat recovery systems that capture waste heat and use it to preheat incoming steel. This helps to reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs.
- Consistent quality: Continuous furnaces can heat steel billets or slabs to a precise temperature, ensuring consistent quality in the finished product. This helps to improve product performance and reduce defects.
- Higher productivity: Continuous furnaces can process large quantities of steel quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. This helps to increase productivity and reduce production costs.
- Customizable settings: Continuous furnaces can be customized to meet specific production requirements, such as varying the temperature profile or adjusting the conveyor speed. This helps to improve process flexibility and adaptability.
- Automated controls: Continuous furnaces are often equipped with advanced automation and control systems that monitor and adjust temperature, pressure, and other variables in real-time, ensuring consistent and reliable operation. This helps to improve process efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Environmental benefits: Continuous furnaces are often designed with low emissions technology, reducing the environmental impact of the production process. This helps to improve environmental sustainability and meet regulatory requirements.